Structure and interactions of the archaeal motility repression module ArnA-ArnB that modulates archaellum gene expression in Sulfolobus acidocaldarius
- PMID: 30902813
- PMCID: PMC6509490
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007709
Structure and interactions of the archaeal motility repression module ArnA-ArnB that modulates archaellum gene expression in Sulfolobus acidocaldarius
Abstract
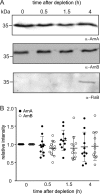
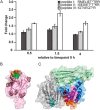
Phosphorylation-dependent interactions play crucial regulatory roles in all domains of life. Forkhead-associated (FHA) and von Willebrand type A (vWA) domains are involved in several phosphorylation-dependent processes of multiprotein complex assemblies. Although well-studied in eukaryotes and bacteria, the structural and functional contexts of these domains are not yet understood in Archaea. Here, we report the structural base for such an interacting pair of FHA and vWA domain-containing proteins, ArnA and ArnB, in the thermoacidophilic archaeon Sulfolobus acidocaldarius, where they act synergistically and negatively modulate motility. The structure of the FHA domain of ArnA at 1.75 Å resolution revealed that it belongs to the subclass of FHA domains, which recognizes double-pSer/pThr motifs. We also solved the 1.5 Å resolution crystal structure of the ArnB paralog vWA2, disclosing a complex topology comprising the vWA domain, a β-sandwich fold, and a C-terminal helix bundle. We further show that ArnA binds to the C terminus of ArnB, which harbors all the phosphorylation sites identified to date and is important for the function of ArnB in archaellum regulation. We also observed that expression levels of the archaellum components in response to changes in nutrient conditions are independent of changes in ArnA and ArnB levels and that a strong interaction between ArnA and ArnB observed during growth on rich medium sequentially diminishes after nutrient limitation. In summary, our findings unravel the structural features in ArnA and ArnB important for their interaction and functional archaellum expression and reveal how nutrient conditions affect this interaction.
Keywords: Archaea; cell motility; protein phosphorylation; signal transduction; transcription regulation.
© 2019 Hoffmann et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

