Multilocus Sequence Analysis, a Rapid and Accurate Tool for Taxonomic Classification, Evolutionary Relationship Determination, and Population Biology Studies of the Genus Shewanella
- PMID: 30902862
- PMCID: PMC6532039
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.03126-18
Multilocus Sequence Analysis, a Rapid and Accurate Tool for Taxonomic Classification, Evolutionary Relationship Determination, and Population Biology Studies of the Genus Shewanella
Abstract
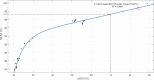
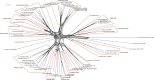
The genus Shewanella comprises a group of marine-dwelling species with worldwide distribution. Several species are regarded as causative agents of food spoilage and opportunistic pathogens of human diseases. In this study, a standard multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA) based on six protein-coding genes (gyrA, gyrB, infB, recN, rpoA, and topA) was established as a rapid and accurate identification tool in 59 Shewanella type strains. This method yielded sufficient resolving power in regard to enough informative sites, adequate sequence divergences, and distinct interspecies branches. The stability of phylogenetic topology was supported by high bootstrap values and concordance with different methods. The reliability of the MLSA scheme was further validated by identical phylogenies and high correlations of genomes. The MLSA approach provided a robust system to exhibit evolutionary relationships in the Shewanella genus. The split network tree proposed twelve distinct monophyletic clades with identical G+C contents and high genetic similarities. A total of 86 tested strains were investigated to explore the population biology of the Shewanella genus in China. The most prevalent Shewanella species was Shewanella algae, followed by Shewanella xiamenensis, Shewanella chilikensis, Shewanella indica, Shewanella seohaensis, and Shewanella carassii The strains frequently isolated from clinical and food samples highlighted the importance of increasing the surveillance of Shewanella species. Based on the combined genetic, genomic, and phenotypic analyses, Shewanella upenei should be considered a synonym of S. algae, and Shewanella pacifica should be reclassified as a synonym of Shewanella japonicaIMPORTANCE The MLSA scheme based on six housekeeping genes (HKGs) (gyrA, gyrB, infB, recN, rpoA, and topA) is well established as a reliable tool for taxonomic, evolutionary, and population diversity analyses of the genus Shewanella in this study. The standard MLSA method allows researchers to make rapid, economical, and precise identification of Shewanella strains. The robust phylogenetic network of MLSA provides profound insight into the evolutionary structure of the genus Shewanella The population genetics of Shewanella species determined by the MLSA approach plays a pivotal role in clinical diagnosis and routine monitoring. Further studies on remaining species and genomic analysis will enhance a more comprehensive understanding of the microbial systematics, phylogenetic relationships, and ecological status of the genus Shewanella.
Keywords: Shewanella; evolutionary relationship; identification; multilocus sequence analysis; population biology; taxonomic classification.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures



References
-
- MacDonell MT, Colwell RR. 1985. Phylogeny of the Vibrionaceae and recommendation for two new genera, Listonella and Shewanella. Syst Appl Microbiol 6:171–182. doi: 10.1016/S0723-2020(85)80051-5. - DOI
-
- Bowman JP. 2005. Genus XIII. Shewanella MacDonell and Colwell 1986, 355VP (effective publication: MacDonell and Colwell 1985,180), p 480–491. In Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT, Garrity GM (ed), Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, 2nd ed Springer, New York, NY.
-
- Venkateswaran K, Moser DP, Dollhopf ME, Lies DP, Saffarini DA, MacGregor BJ, Ringelberg DB, White DC, Nishijima M, Sano H, Burghardt J, Stackebrandt E, Nealson KH. 1999. Polyphasic taxonomy of the genus Shewanella and description of Shewanella oneidensis sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 49:705–724. doi: 10.1099/00207713-49-2-705. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gauthier G, Gauthier M, Christen R. 1995. Phylogenetic analysis of the genera Alteromonas, Shewanella, and Moritella using genes coding for small-subunit rRNA sequences and division of the genus Alteromonas into two genera, Alteromonas (emended) and Pseudoalteromonas gen. nov., and proposal of twelve new species combinations. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45:755–761. doi: 10.1099/00207713-45-4-755. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

