MRI brain lesions in asymptomatic boys with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy
- PMID: 30902905
- PMCID: PMC6511088
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000007294
MRI brain lesions in asymptomatic boys with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy
Abstract
Objective: To describe the brain MRI findings in asymptomatic patients with childhood cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy (CCALD).
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed a series of biochemically or genetically confirmed cases of adrenoleukodystrophy followed at our institution between 2001 and 2015. We identified and analyzed 219 brain MRIs from 47 asymptomatic boys (median age 6.0 years). Patient age, MRI scan, and brain lesion characteristics (e.g., contrast enhancement, volume, and Loes score) were recorded. The rate of lesion growth was estimated using a linear mixed effect model.
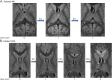
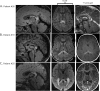
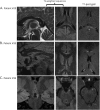
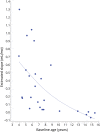
Results: Sixty percent of patients (28/47) showed brain lesions (median Loes score of 3.0 points; range 0.5-11). Seventy-nine percent of patients with CCALD (22/28) had contrast enhancement on first lesional or subsequent MRI. Lesion progression (Loes increase of ≥0.5 point) was seen in 50% of patients (14/28). The rate of lesion growth (mL/mo) was faster in younger patients (r = -0.745; p < 0.0001). Older patients (median age 14.4 y/o) tended to undergo spontaneous arrest of disease. Early lesions grew 46× faster when still limited to the splenium, genu of the corpus callosum, or the brainstem (p = 0.001).
Conclusion: We provide a description of CCALD lesion development in a cohort of asymptomatic boys. Understanding the early stages of CCALD is crucial to optimize treatments for children diagnosed by newborn screening.
© 2019 American Academy of Neurology.
Figures

Comment in
-
Measuring early lesion growth in boys with cerebral demyelinating adrenoleukodystrophy.Neurology. 2019 Apr 9;92(15):691-693. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000007256. Epub 2019 Mar 22. Neurology. 2019. PMID: 30902909 No abstract available.
References
-
- Moser HW, Loes DJ, Melhem ER, et al. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: overview and prognosis as a function of age and brain magnetic resonance imaging abnormality: a study involving 372 patients. Neuropediatrics 2000;31:227–239. - PubMed
-
- Eichler FS, Ren JQ, Cossoy M, et al. Is microglial apoptosis an early pathogenic change in cerebral X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy? Ann Neurol 2008;63:729–742. - PubMed
-
- Korenke GC, Pouwels PJ, Frahm J, et al. Arrested cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy: a clinical and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study in three patients. Pediatr Neurol 1996;15:103–107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
