Efficacy and Safety of Octagam® in Patients With Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy
- PMID: 30903535
- PMCID: PMC6534624
- DOI: 10.1007/s40120-019-0132-5
Efficacy and Safety of Octagam® in Patients With Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy
Abstract
Introduction: Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP) is a debilitating autoimmune neuropathy that is treated with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG). The aim of this retrospective study was to investigate the efficacy and safety of the sucrose-free IVIG Octagam® (Octapharma AG, Lachen, Switzerland) in patients with CIDP.
Methods: Data from 47 patients who received at least one dose of Octagam were collected from the records of 11 centres in France. Efficacy was assessed using Overall Neuropathy Limitation Scale (ONLS). Safety was evaluated using adverse event rates.
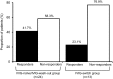
Results: Data from 24 patients who were IVIG naïve (n = 11) or had stopped IVIG ≥ 12 weeks before initiation of Octagam therapy (washout group; n = 13) were included in the efficacy analysis. At 4 months post-initiation of Octagam treatment, 41.7% of patients had improved their functional status (decrease of ≥ 1 ONLS score) with a significant change in the ONLS score from baseline (- 0.42; p = 0.04; signed test). Functional status was reduced in only two patients: one patient in the IVIG-naïve group and one patient in the IVIG-washout group. All 47 patients were included in the safety analysis, which showed that Octagam was well tolerated, with a frequency of 0.04 adverse events per Octagam course. The most common adverse drug reaction was headache.
Conclusions: These real-life results are consistent with the efficacy and safety of IVIG reported in randomised controlled studies. A long-term prospective study of Octagam in patients with CIDP is warranted.
Funding: Octapharma, France SAS.
Keywords: Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy; Immunoglobulins; Immunotherapy; Octagam®; Peripheral nervous system disease.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

