Release and transformation of ZnO nanoparticles used in outdoor surface coatings for UV protection
- PMID: 30903905
- PMCID: PMC6770995
- DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.189
Release and transformation of ZnO nanoparticles used in outdoor surface coatings for UV protection
Abstract
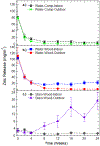
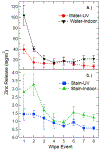
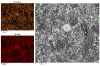
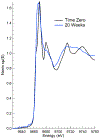
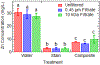
A major area of growth for "nano-enabled" products has been the addition of nanoparticles (NPs) to surface coatings including paints, stains and sealants. Zinc oxide (ZnO) NPs, long used in sunscreens and sunblocks, have found growing use in surface coating formulations to increase their UV resistance, especially on outdoor products. In this work, ZnO NPs, marketed as an additive to paints and stains, were dispersed in Milli-Q water and a commercial deck stain. Resulting solutions were applied to either Micronized-Copper Azole (MCA) pressure treated lumber or a commercially available composite decking. A portion of coated surfaces were placed outdoors to undergo environmental weathering, while the remaining samples were stored indoors to function as experimental controls. Weathered and control treatments were subsequently sampled periodically for 6 months using a simulated dermal contact method developed by the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC). The release of ZnO NPs, and their associated degradation products, was determined through sequential filtration, atomic spectroscopy, X-Ray Absorption Fine Structure Spectroscopy, and electron microscopy. Across all treatments, the percentage of applied zinc released through simulated dermal contact did not exceed 4%, although transformation and release of zinc was highly dependent on dispersion medium. For MCA samples weathered outdoors, water-based applications released significantly more zinc than stain-based, 180 ± 28, and 65 ± 9 mg/m2 respectively. Moreover, results indicate that the number of contact events drives material release.
Keywords: Exposure; Nano-enabled; Nanomaterial; Surface coating; XAFS; Zinc.
Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transformation and release of nanoparticle additives & byproducts from commercially available surface coatings on pressure treated lumber via dermal contact.Sci Total Environ. 2019 Dec 1;694:133669. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133669. Epub 2019 Jul 30. Sci Total Environ. 2019. PMID: 31382174 Free PMC article.
-
Cutting-edge developments in zinc oxide nanoparticles: synthesis and applications for enhanced antimicrobial and UV protection in healthcare solutions.RSC Adv. 2024 Jul 3;14(29):20992-21034. doi: 10.1039/d4ra02452d. eCollection 2024 Jun 27. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38962092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dermal transfer and environmental release of CeO2 nanoparticles used as UV inhibitors on outdoor surfaces: Implications for human and environmental health.Sci Total Environ. 2018 Feb 1;613-614:714-723. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.050. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Sci Total Environ. 2018. PMID: 28938214 Free PMC article.
-
Release and transformation of nanoparticle additives from surface coatings on pristine & weathered pressure treated lumber.Sci Total Environ. 2020 Oct 1;737:139451. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139451. Epub 2020 May 20. Sci Total Environ. 2020. PMID: 32512308 Free PMC article.
-
Titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles in sunscreens: focus on their safety and effectiveness.Nanotechnol Sci Appl. 2011 Oct 13;4:95-112. doi: 10.2147/NSA.S19419. Nanotechnol Sci Appl. 2011. PMID: 24198489 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Modern Science and Technology: Multifunctional Roles in Healthcare, Environmental Remediation, and Industry.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025 May 17;15(10):754. doi: 10.3390/nano15100754. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40423144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ZnO nanoparticles induce acute arrhythmia and heart failure in mice by disturbing cardiac ion channels.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 May 30;12:1569265. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1569265. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40520930 Free PMC article.
-
Transformation and release of nanoparticle additives & byproducts from commercially available surface coatings on pressure treated lumber via dermal contact.Sci Total Environ. 2019 Dec 1;694:133669. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133669. Epub 2019 Jul 30. Sci Total Environ. 2019. PMID: 31382174 Free PMC article.
-
Variation in zinc release from surface coatings as a function of methodology.Sci Total Environ. 2021 Sep 20;788:147907. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147907. Epub 2021 May 21. Sci Total Environ. 2021. PMID: 34134384 Free PMC article.
-
Cutting-edge developments in zinc oxide nanoparticles: synthesis and applications for enhanced antimicrobial and UV protection in healthcare solutions.RSC Adv. 2024 Jul 3;14(29):20992-21034. doi: 10.1039/d4ra02452d. eCollection 2024 Jun 27. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38962092 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Al-Kattan A, Wichser A, Vonbank R, Brunner S, Ulrich A, Zuin S, et al. Characterization of materials released into water from paint containing nano-SiO2. Chemosphere 2015; 119: 1314–1321. - PubMed
-
- Al-Kattan A, Wichser A, Vonbank R, Brunner S, Ulrich A, Zuin S, et al. Release of TiO2 from paints containing pigment-TiO2 or nano-TiO2 by weathering. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts 2013; 15: 2186–2193. - PubMed
-
- Baek S, Joo SH, Kumar N, Toborek M. Antibacterial effect and toxicity pathways of industrial and sunscreen ZnO nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering.
-
- Bian S-W, Mudunkotuwa IA, Rupasinghe T, Grassian VH. Aggregation and Dissolution of 4 nm ZnO Nanoparticles in Aqueous Environments: Influence of pH, Ionic Strength, Size, and Adsorption of Humic Acid. Langmuir 2011; 27: 6059–6068. - PubMed
-
- Clar JG, Platten WE, Baumann EJ, Remsen A, Harmon SM, Bennett-Stamper CL, et al. Dermal transfer and environmental release of CeO 2 nanoparticles used as UV inhibitors on outdoor surfaces: Implications for human and environmental health. Science of The Total Environment 2018; 613: 714–723. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

