Multicentre, prospective, randomised, controlled, blinded-endpoint study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pterygopalatine ganglion pulsed radiofrequency treatment for cluster headache: study protocol
- PMID: 30904875
- PMCID: PMC6475260
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-026608
Multicentre, prospective, randomised, controlled, blinded-endpoint study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pterygopalatine ganglion pulsed radiofrequency treatment for cluster headache: study protocol
Abstract
Introduction: Single-centre reports on small groups of patients have shown that pterygopalatine ganglion pulsed radiofrequency treatment in patients with refractory cluster headache (CH) can quickly relieve pain without significant side effects. However, a randomised controlled trial is still necessary to evaluate whether pterygopalatine ganglion pulsed radiofrequency (PRF) treatment is a viable treatment option for patients with CH who are not responding to drug treatment.
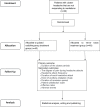
Methods and analysis: This investigation is a multicentre, prospective, randomised, controlled, blinded-endpoint study. We will enrol 80 patients with CH who are not responding to medication. The enrolled patients will be randomly divided into two groups: the nerve block (NB) group and the PRF group. All patients will undergo CT-guided pterygopalatine ganglion puncture. A mixture containing steroids and local anaesthetics will be slowly injected into the patients in the NB group. The patients in the PRF group will be treated with PRF at 42°C for 360 s. After treatment, the duration of cluster periods; degree of pain during headache attacks; frequency of headache attacks; duration of each headache attack; dose of auxiliary analgesic drugs; duration of remission; degree of patient satisfaction; effectiveness rates at 1 day, 3 days, 1 week, 2 weeks, 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, and 1 year after the procedure; and intraoperative and postoperative adverse events will be compared between the two groups.
Ethics and dissemination: This study was approved by the institutional ethics committee of the Beijing Tiantan Hospital (approval number: KY 2018-027-02). The results of the study will be published in peer-reviewed journals, and the findings will be presented at scientific meetings.
Trial registration number: NCT03567590; Pre-results.
Keywords: cluster headache; protocol; pulsed radiofrequency; randomized controlled trial.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2018. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
References
-
- Weaver-Agostoni J. Cluster headache. Am Fam Physician 2013;88:122–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical