Agonist-dependent development of delta opioid receptor tolerance in the colon
- PMID: 30904952
- PMCID: PMC11105391
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-019-03077-6
Agonist-dependent development of delta opioid receptor tolerance in the colon
Abstract
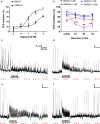
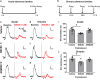
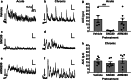
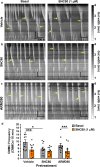
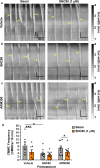
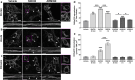
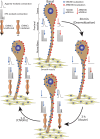
The use of opioid analgesics is severely limited due to the development of intractable constipation, mediated through activation of mu opioid receptors (MOR) expressed by enteric neurons. The related delta opioid receptor (DOR) is an emerging therapeutic target for chronic pain, depression and anxiety. Whether DOR agonists also promote sustained inhibition of colonic transit is unknown. This study examined acute and chronic tolerance to SNC80 and ARM390, which were full and partial DOR agonists in neural pathways controlling colonic motility, respectively. Excitatory pathways developed acute and chronic tolerance to SNC80, whereas only chronic tolerance developed in inhibitory pathways. Both pathways remained functional after acute or chronic ARM390 exposure. Propagating colonic motor patterns were significantly reduced after acute or chronic SNC80 treatment, but not by ARM390 pre-treatment. These findings demonstrate that SNC80 has a prolonged inhibitory effect on propagating colonic motility. ARM390 had no effect on motor patterns and thus may have fewer gastrointestinal side-effects.
Keywords: Colon motility; Endocytosis; Enteric nervous system; GPCR regulation; Opioid receptor.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

