Small-molecule inhibitors as potential therapeutics and as tools to understand the role of phospholipases A2
- PMID: 30905350
- PMCID: PMC7106526
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2018.08.009
Small-molecule inhibitors as potential therapeutics and as tools to understand the role of phospholipases A2
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Small-molecule inhibitors as potential therapeutics and as tools to understand the role of phospholipases A2" [Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 1864/6 2019 941-956].Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2019 Nov;1864(11):1681. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2019.06.009. Epub 2019 Jun 17. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2019. PMID: 31221540 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
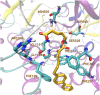
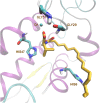
Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) enzymes are involved in various inflammatory pathological conditions including arthritis, cardiovascular and autoimmune diseases. The regulation of their catalytic activity is of high importance and a great effort has been devoted in developing synthetic inhibitors. We summarize the most important small-molecule synthetic PLA2 inhibitors developed to target each one of the four major types of human PLA2 (cytosolic cPLA2, calcium-independent iPLA2, secreted sPLA2, and lipoprotein-associated LpPLA2). We discuss recent applications of inhibitors to understand the role of each PLA2 type and their therapeutic potential. Potent and selective PLA2 inhibitors have been developed. Although some of them have been evaluated in clinical trials, none reached the market yet. Apart from their importance as potential medicinal agents, PLA2 inhibitors are excellent tools to unveil the role that each PLA2 type plays in cells and in vivo. Modern medicinal chemistry approaches are expected to generate improved PLA2 inhibitors as new agents to treat inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: Clinical trials; Inflammation; Inhibitors; Phospholipase A(2).
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


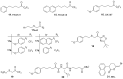
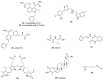


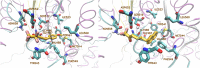
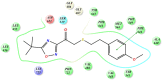
References
-
- Imming P., Sinning C., Meyer A. Drugs, their targets and the nature and number of drug targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006;5:821–834. - PubMed
-
- Holdgate G.A., Meek T.D., Grimley R.L. Mechanistic enzymology in drug discovery: a fresh perspective. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018;17:115–132. - PubMed
-
- Nicolaou A., Kokotos G. The Oily Press; Bridgewater, England: 2004. Bioactive Lipids.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

