Artificial Neural Network: Understanding the Basic Concepts without Mathematics
- PMID: 30906397
- PMCID: PMC6428006
- DOI: 10.12779/dnd.2018.17.3.83
Artificial Neural Network: Understanding the Basic Concepts without Mathematics
Abstract
Machine learning is where a machine (i.e., computer) determines for itself how input data is processed and predicts outcomes when provided with new data. An artificial neural network is a machine learning algorithm based on the concept of a human neuron. The purpose of this review is to explain the fundamental concepts of artificial neural networks.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence; Deep Learning; Machine Learning; Neural Networks.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
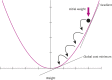
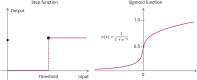

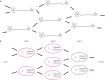
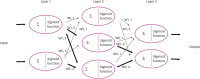
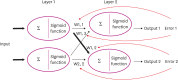
References
-
- Samuel AL. Some studies in machine learning using the game of checkers. IBM J Res Develop. 1959;3:210–229.
-
- Koza JR, Bennett FH, 3rd, Andre D, Keane MA. Automated design of both the topology and sizing of analog electrical circuits using genetic programming. In: Gero JS, Sudweeks F, editors. Artificial Intelligence in Design. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic; 1996. pp. 151–170.
-
- Rashid T. Make Your Own Neural Network. 1st ed. North Charleston, SC: CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform; 2016.
-
- Haykin S, Haykin SS. Neural Networks and Learning Machines. 3rd ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall; 2009.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

