Gastroprotective Effects of Paeonia Extract Mixture HT074 against Experimental Gastric Ulcers in Rats
- PMID: 30906413
- PMCID: PMC6398042
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/3546258
Gastroprotective Effects of Paeonia Extract Mixture HT074 against Experimental Gastric Ulcers in Rats
Abstract
Background: Paeonia extract mixture HT074 is a standardized multiherbal mixture comprising extracts from Inula britannica flowers and Paeonia lactiflora roots, which are used to treat digestive disorders in traditional Korean medicine. This study was focused on elucidating the underlying mechanisms of the gastroprotective effects of HT074 in different gastric ulcer models.
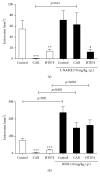
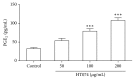
Methods: Gastric lesions were induced in rats by an HCl/EtOH solution, water immersion-restraint stress (WIRS), and indomethacin. Gastric secretions were studied in pylorus-ligated rats, while mucus secretions were assessed by measuring alcian blue-binding capacity of mucus in the rat model of HCl/EtOH-induced gastric ulcer. Additionally, the involvement of nitric oxide (NO) and sulfhydryl compounds in HT074-mediated mucosal protection was elucidated using their inhibitors, i.e., N G -nitro- L-arginine methyl ester hydrochloride (L-NAME) and N-ethylmaleimide (NEM), respectively. Furthermore, the effects on indomethacin-induced cell death and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) levels were assessed in AGS cells.
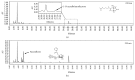
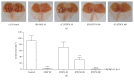
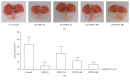
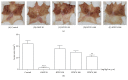
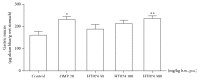
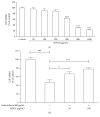
Results: Oral administration of HT074 significantly decreased gastric lesions induced by HCl/EtOH, WIRS, and indomethacin. Furthermore, it significantly decreased the volume, acidity, and total acidity of gastric juice in pylorus-ligated rats and increased the alcian blue-stained gastric mucus in HCl/EtOH-induced gastric ulcer in rats. Pretreatment with NEM abolished the gastroprotective effects of HT074, while L-NAME did not. In AGS cells, HT074 significantly reduced indomethacin-induced cell death and increased the PGE2 levels.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that HT074 has gastroprotective effects against various ulcerogens, including HCl/EtOH, immersion stress, and NSAIDs. These effects are attributed to the inhibition of gastric secretions and preservation of the gastric mucosal barrier by increased mucus production, which is partially mediated through endogenous sulfhydryl compounds and PGE2. Based on these findings, we propose that HT074 may be a promising therapeutic agent for gastritis and gastric ulcer.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

