Assessing biological aging following systemic administration of bFGF-supplemented adipose-derived stem cells with high efficacy in an experimental rat model
- PMID: 30906427
- PMCID: PMC6425125
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.7251
Assessing biological aging following systemic administration of bFGF-supplemented adipose-derived stem cells with high efficacy in an experimental rat model
Abstract
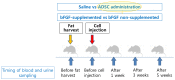
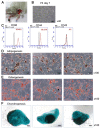
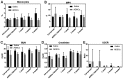
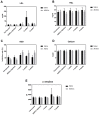
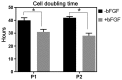
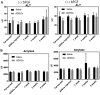
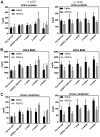
Biological aging (BA) is a tool for comprehensive assessment of individual health status. A rat model was developed for measuring BA by intravenously administering adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) into rats and evaluating several biochemical parameters. In addition, the effect of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) on the differentiation potential of ADSCs was analyzed. A total of 12 male Sprague Dawley rats were divided into autologous ADSC administration (n=6) and saline administration (n=6) groups. The ADSC administration group was further divided into the bFGF supplemented (n=3) and bFGF non-supplemented (n=3) groups. Biochemical parameters and antioxidant potential were evaluated prior to fat harvest and ADSC administration, as well as 1, 3, and 5 weeks following ADSC administration. ADSC administration regulated inflammation, renal and hepatic functions, and levels of antioxidant enzymes. The cell doubling time of the bFGF-supplemented group was shorter (P=0.0001) than that of the bFGF non-supplemented group. Renal and hepatic functions were maintained with bFGF supplementation, which possibly enhanced the effect of ADSCs. The rat model developed in the present study may promote better understanding of BA in the context of bFGF-supplemented ADSC administration.
Keywords: adipose-derived stem cell; basic fibroblast growth factor; biochemical parameter; biologic aging; rat model.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biological Aging Parameters Can Be Improved After Autologous Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Injection.J Craniofac Surg. 2019 May/Jun;30(3):652-658. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000004932. J Craniofac Surg. 2019. PMID: 30394974
-
Injection of basic fibroblast growth factor together with adipose-derived stem cell transplantation: improved cardiac remodeling and function in myocardial infarction.Clin Exp Med. 2016 Nov;16(4):539-550. doi: 10.1007/s10238-015-0383-0. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Clin Exp Med. 2016. PMID: 26349680
-
Adipose-derived stem cells improve erectile function partially through the secretion of IGF-1, bFGF, and VEGF in aged rats.Andrology. 2018 May;6(3):498-509. doi: 10.1111/andr.12483. Epub 2018 Mar 30. Andrology. 2018. PMID: 29603682
-
Comparison between subcutaneous injection of basic fibroblast growth factor-hydrogel and intracavernous injection of adipose-derived stem cells in a rat model of cavernous nerve injury.Urology. 2014 Nov;84(5):1248.e1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2014.07.028. Epub 2014 Oct 24. Urology. 2014. PMID: 25443945
-
Periurethral injection of autologous adipose-derived stem cells with controlled-release nerve growth factor for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence in a rat model.Eur Urol. 2011 Jan;59(1):155-63. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2010.10.038. Epub 2010 Oct 26. Eur Urol. 2011. PMID: 21050657
Cited by
-
Licochalcone A activation of glycolysis pathway has an anti-aging effect on human adipose stem cells.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Dec 3;13(23):25180-25194. doi: 10.18632/aging.203734. Epub 2021 Dec 3. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34862330 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Population Prospects: The 2017 Revision. Executive Summary. United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. https://esa.un.org/unpd/wpp/publications/files/wpp2017_keyfindings.pdf. [Jun 21;2017 ];2017
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
