Acetic acid alleviates the inflammatory response and liver injury in septic mice by increasing the expression of TRIM40
- PMID: 30906467
- PMCID: PMC6425238
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.7274
Acetic acid alleviates the inflammatory response and liver injury in septic mice by increasing the expression of TRIM40
Abstract
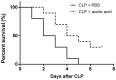
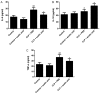
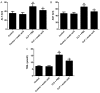
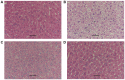
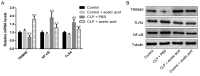
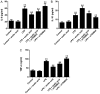
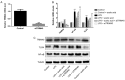
Sepsis remains a significant health care issue in clinical practice due to its high mortality rate and healthcare cost, despite extensive efforts to better understand the pathophysiology of sepsis. The systemic inflammatory response often leads to severe liver injury, even acute liver dysfunction and failure. Acetic acid, as a type of chemical compound, has been reported to be an emerging drug for improving metabolic syndrome and inhibiting inflammation in rats and human. To verify the effects of acetic acid in protecting the liver and reducing the inflammatory response, a septic mouse model was established by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP), and then the CLP-model mice were treated with acetic acid or PBS. Following the treatment, it was determined that, in CLP-model mice, acetic acid could alleviate the inflammatory response by decreasing the expression of cytokines including interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α. Additionally, acetic acid also alleviated the liver injury, and the levels of alanine aminotransaminase, aspartate aminotransferase, Toll-like receptor (TLR)4 and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) were decreased. The expression of tripartite motif-containing protein (TRIM)40 was also upregulated significantly. Therefore, the authors of the current study hypothesized that acetic acid could decrease the inflammatory response by increasing the expression of TRIM40 and TRIM40 may regulate the activity of the TLR4 signaling pathway. To further illustrate the interaction between TRIM40 and the TLR4 signaling pathway, the authors collected macrophages from the peritoneal cavity by intraperitoneally administering mice with 5 ml ice-cold normal saline. Following the collection, peritoneal macrophages were treated with acetic acid, TRIM40 small interfering RNA or PBS. It was demonstrated that acetic acid upregulated the expression of TRIM40. When TRIM40 was silenced, the protective effect of acetic acid would be reversed as well. The results suggested that TRIM40 could act on and downregulate the activity of the TLR4 signaling pathway. TRIM40 is possibly the major target for acetic acid, which may function as a protective factor in septic mice.
Keywords: acetic acid; liver injury; nuclear factor NF-κB; sepsis; tripartite motif-containing protein 40.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Liver injury in septic mice were suppressed by a camptothecin-bile acid conjugate via inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway.Life Sci. 2020 Sep 15;257:118130. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118130. Epub 2020 Jul 22. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32710950
-
[Selectively activating melanocortin 4 receptor acts against rat sepsis-induced acute liver injury via HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016 Aug;32(8):1055-9. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27412936 Chinese.
-
Pterostilbene alleviates polymicrobial sepsis-induced liver injury: Possible role of SIRT1 signaling.Int Immunopharmacol. 2017 Aug;49:50-59. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2017.05.022. Epub 2017 May 25. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28550734
-
Paclitaxel alleviated liver injury of septic mice by alleviating inflammatory response via microRNA-27a/TAB3/NF-κB signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Jan;97:1424-1433. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.11.003. Epub 2017 Dec 14. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29156532
-
[Protective effect of recombinant adult serine protease inhibitor from Trichinella spiralis on sepsis-associated acute kidney injury in mice].Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2020 Aug 24;32(4):361-366. doi: 10.16250/j.32.1374.2020122. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32935509 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Metabolites and Gut Microbes between Patients with Ulcerative Colitis and Healthy Individuals for an Integrative Medicine Approach to Ulcerative Colitis-A Pilot Observational Clinical Study (STROBE Compliant).Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Aug 15;12(8):1969. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12081969. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36010319 Free PMC article.
-
Suspected Permethrin-Containing Powder Bath Poisoning in a Flock of Mountain Quail (Oreortyx pictus).Animals (Basel). 2025 May 15;15(10):1428. doi: 10.3390/ani15101428. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427305 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Roles of MHC Class I Region-Encoded E3 Ubiquitin Ligases in Innate Immunity.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 10;12:687102. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.687102. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34177938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Study on the preparation of compound mold enhanced Xiaoqu and its effect on the yield and flavor of Qingxiangxing baijiu.Food Chem X. 2025 Jul 3;29:102721. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2025.102721. eCollection 2025 Jul. Food Chem X. 2025. PMID: 40686889 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium Alginate Prevents Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Modulating the Gut-Liver Axis in High-Fat Diet-Fed Rats.Nutrients. 2022 Nov 16;14(22):4846. doi: 10.3390/nu14224846. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36432531 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D, Gerlach H, Opal SM, Sevransky JE, Sprung CL, Douglas IS, Jaeschke R, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012. Crit Care Med. 2013;41:580–637. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31827e83af. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
