CD147 mediates transforming growth factor-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell invasion in squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue
- PMID: 30906472
- PMCID: PMC6425230
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.7230
CD147 mediates transforming growth factor-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell invasion in squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue
Abstract
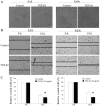
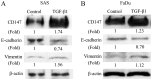
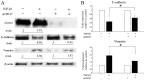
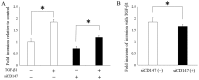
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a physiological process in which epithelial cells attain the motile and invasive characteristics of mesenchymal cells, which results in the development of increased migratory and invasive cell behavior, serving as a vital mechanism of cancer progression. Hence, controlling the EMT for cancer treatment, including head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), is imperative. Among EMT-associated factors, transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) is a well-established potent inducer. Recent research has revealed that CD147, a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, promotes the EMT. However, the role of CD147 in the EMT and the following tumorigenicity in HNSCC has not been completely elucidated. This study aims to investigate the role of CD147 in the EMT and related tumorigenicity in HNSCC. The present study used two HNSCC cell lines, SAS and FaDu, for in vitro studies. In HNSCC cells, TGF-β1 induced spindle-shaped morphological changes, and western blot analysis revealed that TGF-β1 induced changes in EMT markers, downregulation of vimentin, and upregulation of E-cadherin, yet increased CD147. In addition, TGF-β1 increased cell migration in HNSCC cells. However, a TGF-β1-induced alteration in EMT makers was attenuated with CD147 silencing by small interfering RNA (siRNA) in SAS cells. In addition, the TGF-β1-induced cell invasion of SAS was attenuated with CD147 silencing. In conclusion, the present study suggests that CD147 mediates TGF-β1-induced EMT and tumorigenicity in HNSCC. Hence, CD147 may serve as a vital therapeutic target in HNSCC.
Keywords: CD147; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; head and neck cancer; invasion; migration; transforming growth factor-β1.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
