Changes in serum LDL, PCSK9 and microRNA-122 in patients with chronic HCV infection receiving Daclatasvir/Asunaprevir
- PMID: 30906544
- PMCID: PMC6403470
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2019.1189
Changes in serum LDL, PCSK9 and microRNA-122 in patients with chronic HCV infection receiving Daclatasvir/Asunaprevir
Abstract
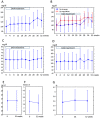
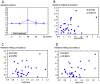
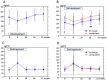
The present study evaluated the changes in lipid profile, and the associations between serum protein convertase subtilisin/kexin 9 (PCSK9), microRNA (miR)122 and low-density lipoprotein variation following treatment of hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 1b infection with Daclatasvir/Asunaprevir. A total of 39 patients with HCV genotype 1b infection with chronic hepatitis received a 24-week treatment regimen of Daclatasvir/Asunaprevir. Laboratory data were obtained for each subject every 4 weeks during treatment and every 12 weeks after treatment. Serum miR122 and PCSK9 were measured at the start of treatment (week 0), end of treatment (week 24), 4 weeks after the end of treatment (week 28), 12 weeks after the end of treatment (week 36) and 28 weeks after the end of treatment (week 52). LDL was increased at week 4 after the start of treatment to week 52. The increased LDL/HDL ratio at week 52 compared with week 4 was also associated with relative miR122 at week 52. At week 4, PCSK9-active form (A) was lower than that at other time points, and PCSK9-inactive form (I) exhibited the greatest increase. At week 52, PCSK9-A was higher than that during treatment, but PCSK9-I level at week 52 did not markedly differ from that any time point except for week 4. Relative miR122 at week 4 was associated with increased PCSK9-A at weeks 36 and 52 from the start of DAA. In summary, treatment of HCV with Daclatasvir/Asunaprevir resulted in elevated LDL, and relative miR122 and PCSK9-A levels in serum appeared to have some association with LDL increase.
Keywords: direct acting anti-virals; hepatitis C virus; low-density lipoprotein; microRNA122; protein convertase subtilisin/kexin 9.
Figures
References
-
- Ferri C, Sebastiani M, Giuggioli D, Colaci M, Fallahi P, Piluso A, Antonelli A, Zignego AL. Hepatitis C virus syndrome: A constellation of organ- and non-organ specific autoimmune disorders, B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, and cancer. World J Hepatol. 2015;7:327–343. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i3.327. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chayama K, Takahashi S, Toyota J, Karino Y, Ikeda K, Ishikawa H, Watanabe H, McPhee F, Hughes E, Kumada H. Dual therapy with the nonstructural protein 5A inhibitor, daclatasvir, and the nonstructural protein 3 protease inhibitor, asunaprevir, in hepatitis C virus genotype 1b-infected null responders. Hepatology. 2012;55:742–748. doi: 10.1002/hep.24724. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
