Surgical management of chronic diaphragmatic hernias
- PMID: 30906583
- PMCID: PMC6389560
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2019.01.54
Surgical management of chronic diaphragmatic hernias
Abstract
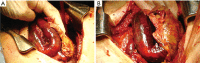
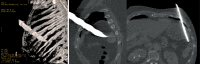
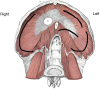
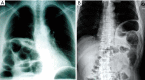
Chronic diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) is an uncommon disease which may be associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Antecedent (even many months or years before CDH development) blunt or penetrating thoracic/thoraco-abdominal trauma is generally recognized. A wide spectrum of different mechanisms of injury, timing in presentation, size of the diaphragmatic defect, types and amount of abdominal viscera herniated into the chest cavity, clinical symptoms are observed in CDHs. Thoracic and abdominal CT scan (with coronal, axial and sagittal reconstructions) is the best diagnostic tool; sometimes thoracic MRI is needed to better define the extent of the diaphragmatic defect and the number of abdominal organs displaced into the chest cavity. Surgery (sometimes urgent) represents the treatment of choice for CDH; diaphragmatic hernia direct repair with a tension-free suture is generally attempted; in case of very large defects or when a tension-free suture is deemed unfeasible, the use of prosthesis is recommended. This review article will discuss about CDH aetiology, clinical presentation diagnosis and surgical treatment.
Keywords: Diaphragm; chronic; hernia; injury; trauma.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




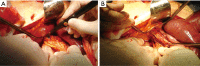
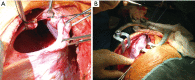

References
-
- Sennertus RC. Diaphragmatic hernia produced by a penetrating wound. Edinburgh Med Surg J 1840;53:104.
-
- Carter BN, Giuseffi J, Felson B. Traumatic diaphragmatic hernia. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther 1951;65:56-72. - PubMed
