Therapeutic Effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine on a Rat Model of Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion
- PMID: 30906588
- PMCID: PMC6398022
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/9521379
Therapeutic Effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine on a Rat Model of Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion
Abstract
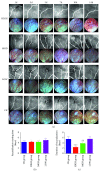
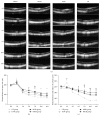
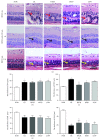
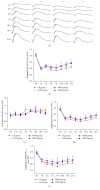
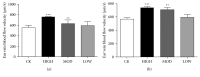
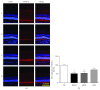
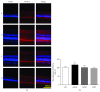
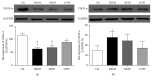
Branch retinal vein occlusion (BRVO) is a common retinal vascular disorder leading to visual impairment. Currently, the general strategies for BRVO are symptomatic therapies. Cardiovascular aspects are essential risk factors for BRVO. The traditional Chinese medicine hexuemingmu (HXMM), consisting of tanshinol and baicalin, dilates the vasculature and accelerates microcirculation. Therefore, the aim of this study was to determine the efficacy and possible mechanism of HXMM in a BRVO rat model established by laser photocoagulation. Successful BRVO rat models were treated with different doses of HXMM. Fundus photography and fluorescein fundus angiography (FFA) of the animals were applied. The retinal layers were measured by optical coherence tomography (OCT). Full-field electroretinography (ffERG) was applied to evaluate the retinal function. The ear vein flow velocity was measured via a microcirculation detector. The expression of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF-α) was measured via western blotting and immunofluorescent staining. Our study found that retinal edema predominantly occurred in the inner nuclear layer (INL) and outer nuclear layer (ONL). The retinal edema of the treated groups was significantly relieved in the early stage of BRVO as visualized via OCT detection and HE staining. The amplitudes of the b wave and oscillatory potentials (OPs) waves of ffERG in the treated groups were increased compared with those of the control group at several detection points (3, 5, 7, 10, 14, and 21 d postocclusion). The expression of VEGF-α was reduced in the treated groups at an early stage of BRVO. Furthermore, the ear vein flow velocity of the HXMM treatment groups was faster than that of the control group. Thus, our study indicates that the traditional Chinese medicine HXMM could ameliorate retinal edema and rescue the retinal structure and function in BRVO models through promoting occluded vein recanalization, improving microcirculation, and regulating the expression of VEGF-α.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protective effects of hydrogen gas in a rat model of branch retinal vein occlusion via decreasing VEGF-α expression.BMC Ophthalmol. 2019 May 16;19(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s12886-019-1105-2. BMC Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31096936 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effect of minocycline in a rat model of branch retinal vein occlusion.Exp Eye Res. 2013 Aug;113:105-16. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2013.05.018. Epub 2013 Jun 5. Exp Eye Res. 2013. PMID: 23748101
-
Natural history and histology in a rat model of laser-induced photothrombotic retinal vein occlusion.Curr Eye Res. 2008 Apr;33(4):365-76. doi: 10.1080/02713680801939318. Curr Eye Res. 2008. PMID: 18398711
-
The Diagnosis and Treatment of Branch Retinal Vein Occlusions: An Update.Biomedicines. 2025 Jan 5;13(1):105. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13010105. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 39857689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokines and the Pathogenesis of Macular Edema in Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion.J Ophthalmol. 2019 May 2;2019:5185128. doi: 10.1155/2019/5185128. eCollection 2019. J Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31191997 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Network Pharmacology-Based Approach to Comparatively Predict the Active Ingredients and Molecular Targets of Compound Xueshuantong Capsule and Hexuemingmu Tablet in the Treatment of Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Mar 5;2021:6642600. doi: 10.1155/2021/6642600. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 33747106 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of hydrogen gas in a rat model of branch retinal vein occlusion via decreasing VEGF-α expression.BMC Ophthalmol. 2019 May 16;19(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s12886-019-1105-2. BMC Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31096936 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in collateral vessel formation after experimental retinal vein occlusion in spontaneously hypertensive rats and wild-type rats.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 1;10(6):e27160. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27160. eCollection 2024 Mar 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38509953 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of patients with central serous chorioretinopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 21;19(6):e0304972. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304972. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38905170 Free PMC article.
-
Potential mechanism of Achyranthis bidentatae radix plus semen vaccariae granules in the treatment of diabetes mellitus-induced erectile dysfunction in rats utilizing combined experimental model and network pharmacology.Pharm Biol. 2021 Dec;59(1):547-556. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2021.1920621. Pharm Biol. 2021. PMID: 33962551 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Noma H., Funatsu H., Harino S., et al. Pathogenesis of macular edema associated with branch retinal vein occlusion and strategy for treatment. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2010;114(7):577–591. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

