Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) Induced Splenic Infarction in Breast Cancer Patient Treated with Dose-Dense Chemotherapy Regimen
- PMID: 30906610
- PMCID: PMC6393871
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/8174986
Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) Induced Splenic Infarction in Breast Cancer Patient Treated with Dose-Dense Chemotherapy Regimen
Abstract
Introduction: Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) is commonly used for prevention and treatment of febrile neutropenia among solid tumor patients. It is considered an effective and relatively safe supportive care medication; however, it can cause rare and serious side effects such as spleen rupture or infarction.
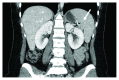
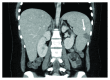
Case presentation: We are reporting a case of a 27-year-old female with breast cancer who has been treated with dose-dense chemotherapy and received colony-stimulating factor as primary prevention of febrile neutropenia that was complicated halfway through with splenic infarction. This finding was confirmed by computed tomography (CT) scan and splenic biopsy. Management was conservative without the need of surgical intervention.
Conclusion: Although splenic infarction is an extremely rare side effect of G-CSF, it can be a serious complication that should be recognized, monitored, and managed carefully.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Caught in the Crossfire: A Case of Splenic Infarction Amid G-CSF therapy in Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukaemia.Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2025 Feb 7;12(3):005007. doi: 10.12890/2025_005007. eCollection 2025. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2025. PMID: 40051744 Free PMC article.
-
Splenic rupture, secondary to G-CSF use for chemotherapy induced neutropenia: a case report and review of literature.Cases J. 2008 Dec 24;1(1):418. doi: 10.1186/1757-1626-1-418. Cases J. 2008. PMID: 19108744 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the effects of pegylated granulocyte-colony stimulating factor and granulocyte-colony stimulating factor on cytopenia induced by dose-dense chemotherapy in breast cancer patients.J Res Med Sci. 2018 Aug 23;23:73. doi: 10.4103/jrms.JRMS_463_17. eCollection 2018. J Res Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30181755 Free PMC article.
-
2010 update of EORTC guidelines for the use of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor to reduce the incidence of chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia in adult patients with lymphoproliferative disorders and solid tumours.Eur J Cancer. 2011 Jan;47(1):8-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2010.10.013. Epub 2010 Nov 20. Eur J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21095116
-
Colony-stimulating factors for the management of neutropenia in cancer patients.Drugs. 2002;62 Suppl 1:1-15. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200262001-00001. Drugs. 2002. PMID: 12479591 Review.
Cited by
-
Atraumatic idiopathic splenic rupture induced by granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) for the treatment of pancytopenia, managed successfully by laparoscopic splenectomy.BMJ Case Rep. 2020 Apr 9;13(4):e232411. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2019-232411. BMJ Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32276997 Free PMC article.
-
The role of granulocyte colony‑stimulating factor in breast cancer development: A review.Mol Med Rep. 2020 May;21(5):2019-2029. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11017. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32186767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vertebral fracture and splenomegaly in a head and neck cancer producing granulocyte colony-stimulating factor: A case report of systemic complications associated with a cytokine-producing solid tumor.Mol Clin Oncol. 2021 Oct;15(4):202. doi: 10.3892/mco.2021.2364. Epub 2021 Aug 8. Mol Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34462658 Free PMC article.
-
Caught in the Crossfire: A Case of Splenic Infarction Amid G-CSF therapy in Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukaemia.Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2025 Feb 7;12(3):005007. doi: 10.12890/2025_005007. eCollection 2025. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2025. PMID: 40051744 Free PMC article.
-
Glycolytic neutrophils accrued in the spleen compromise anti-tumour T cell immunity in breast cancer.Nat Metab. 2023 Aug;5(8):1408-1422. doi: 10.1038/s42255-023-00853-4. Epub 2023 Aug 10. Nat Metab. 2023. PMID: 37563468
References
-
- Taplitz R. A., Kennedy E. B., Bow E. J., et al. Outpatient management of fever and neutropenia in adults treated for malignancy: American Society of Clinical Oncology and Infectious Diseases Society of America clinical practice guideline update. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2018;36(14):1443–1453. doi: 10.1200/jco.2017.77.6211. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

