Pulmonary nodular lymphoid hyperplasia: a rare benign disease with malignant mask
- PMID: 30906747
- PMCID: PMC6389570
- DOI: 10.21037/atm.2018.12.59
Pulmonary nodular lymphoid hyperplasia: a rare benign disease with malignant mask
Abstract
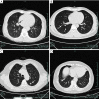
Background: Pulmonary nodular lymphoid hyperplasia (PNLH) is a rare benign disease lacking systematically clinical assessment. This study aims to explore the clinical features of PNLH and evaluate the safety and efficacy of different surgical approaches for PNLH.
Methods: Patients with confirmed PNLH in our department between March 2007 and August 2017 were retrospectively reviewed. The detail information of patients, including demographic characteristics, medical history, preoperative investigations, perioperative findings, postoperative conditions, and recurrence status, was collected and analyzed.
Results: A total of 67 patients with PNLH were diagnosed in our department, and 15 of them were suspected to have lung cancer by radiological examination before the surgery. 43 of 67 patients underwent sublobar resection and 24 patients underwent lobectomy. Compared with the lobectomy, sublobar resection showed more significant advantages in operation time (P<0.001), blood loss (P=0.001), volume of chest drainage (P=0.007), duration of chest drainage (P=0.001) and postoperative hospital stay (P=0.001).
Conclusions: The diagnosis of PNLH before operation is challenging and it should be taken into consideration in the differential diagnosis of lung nodules. Compared with lobectomy, sublobar resection is an alternative approach for the treatment of PNLH.
Keywords: Pulmonary nodular lymphoid hyperplasia (PNLH); diagnosis; lobectomy; sublobar resection.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
