Inhibition of HDAC3 Ameliorates Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in Diabetic Mice In Vivo and In Vitro
- PMID: 30906786
- PMCID: PMC6393870
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/8520856
Inhibition of HDAC3 Ameliorates Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in Diabetic Mice In Vivo and In Vitro
Abstract
Background: A substantial increase in histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) expression is implicated in the pathological process of diabetes and stroke. However, it is unclear whether HDAC3 plays an important role in diabetes complicated with stroke. We aimed to explore the role and the potential mechanisms of HDAC3 in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury in diabetic state.
Methods: Diabetic mice were subjected to 1 h ischemia, followed by 24 h reperfusion. PC12 cells were exposed to high glucose for 24 h, followed by 3 h of hypoxia and 6 h of reoxygenation (H/R). Diabetic mice received RGFP966 (the specific HDAC3 inhibitor) or vehicle 30 minutes before the middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO), and high glucose-incubated PC12 cells were pretreated with RGFP966 or vehicle 6 h before H/R.
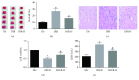
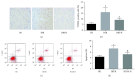
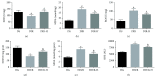
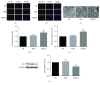
Results: HDAC3 inhibition reduced the cerebral infarct volume, ameliorated pathological changes, improved the cell viability and cytotoxicity, alleviated apoptosis, attenuated oxidative stress, and enhanced autophagy in cerebral I/R injury model in diabetic state in vivo and in vitro. Furthermore, we found that the expression of HDAC3 was remarkably amplified, and the Bmal1 expression was notably decreased in diabetic mice with cerebral I/R, whereas this phenomenon was obviously reversed by RGFP966 pretreatment.
Conclusions: These results suggested that the HDAC3 was involved in the pathological process of the complex disease of diabetic stroke. Suppression of HDAC3 exerted protective effects against cerebral I/R injury in diabetic state in vivo and in vitro via the modulation of oxidative stress, apoptosis, and autophagy, which might be mediated by the upregulation of Bmal1.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

