Assessment of the Effects of Pediatric Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder on Family Stress and Well-Being: Development of the IMPACT 1.0 Scale
- PMID: 30906819
- PMCID: PMC6421607
- DOI: 10.1177/2333794X19835645
Assessment of the Effects of Pediatric Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder on Family Stress and Well-Being: Development of the IMPACT 1.0 Scale
Abstract
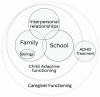
Medications may lessen core symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), yet families continue to report stress and have a low quality of life. Primary care providers manage almost half of all children with ADHD but do not have a brief measure to assess ADHD impacts on family in the context of everyday family life. The IMPACT (Impact Measure of Parenting-Related ADHD Challenges and Treatment) 1.0 Scale was codeveloped with input from parent advisors and administered to 79 parents of children with ADHD. Exploratory factor analysis, correlations with validated instruments, and test-retest reliability were examined. Exploratory factor analysis resulted in 4 subscales (Misbehavior, Siblings, Time, School), which demonstrated moderate to high test-retest reliability. Scale domains were related to severity and change in ADHD symptoms. Significant correlations were found between IMPACT scores, adaptive functioning in the home, and ADHD-related quality of life. The IMPACT 1.0 Scale provides a novel, reliable, and valid method to assess family impact of ADHD.
Keywords: measurement; patient-centered outcomes; pediatrics; primary care; quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Klassen AF, Miller A, Fine S. Health-related quality of life in children and adolescents who have a diagnosis of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics. 2004;114:e541-e547. - PubMed
-
- Williams J, Klinepeter K, Palmes G, Pulley A, Foy JM. Diagnosis and treatment of behavioral health disorders in pediatric practice. Pediatrics. 2004;114:601-606. - PubMed
-
- Hoagwood K, Jensen PS, Feil M, Vitiello B, Bhatara VS. Medication management of stimulants in pediatric practice settings: a national perspective. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 2000;21:322-331. - PubMed
-
- Subcommittee on Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder; Steering Committee on Quality Improvement and Management; Wolraich M, et al. ADHD: clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2011;128:1007-1022. - PMC - PubMed
-
- American Academy of Pediatrics; Subcommittee on Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Committee on Quality Improvement. Clinical practice guideline: treatment of the school-aged child with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics. 2001;108:1033-1044. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources