Emerging roles of lncRNAs in the post-transcriptional regulation in cancer
- PMID: 30906827
- PMCID: PMC6411652
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2019.01.003
Emerging roles of lncRNAs in the post-transcriptional regulation in cancer
Abstract
Accumulating evidence indicates that long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) can play a pivotal role in regulation of diverse cellular processes. In particular, lncRNAs can serve as master gene regulators at transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels, leading to tumorigenesis. In this review, we discuss latest developments in lncRNA-meditated gene expression at the post-transcriptional level, including gene splicing, mRNA stability, protein stability and nuclear trafficking.
Keywords: Alternative splicing; LncRNA; Posttranscriptional regulation; Protein stability; RNA binding proteins; RNA stability.
Figures
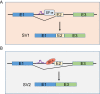
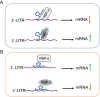
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

