Hypoxia and matrix viscoelasticity sequentially regulate endothelial progenitor cluster-based vasculogenesis
- PMID: 30906859
- PMCID: PMC6426463
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aau7518
Hypoxia and matrix viscoelasticity sequentially regulate endothelial progenitor cluster-based vasculogenesis
Abstract
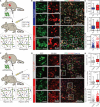
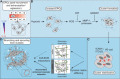
Vascular morphogenesis is the formation of endothelial lumenized networks. Cluster-based vasculogenesis of endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) has been observed in animal models, but the underlying mechanism is unknown. Here, using O2-controllabe hydrogels, we unveil the mechanism by which hypoxia, co-jointly with matrix viscoelasticity, induces EPC vasculogenesis. When EPCs are subjected to a 3D hypoxic gradient ranging from <2 to 5%, they rapidly produce reactive oxygen species that up-regulate proteases, most notably MMP-1, which degrade the surrounding extracellular matrix. EPC clusters form and expand as the matrix degrades. Cell-cell interactions, including those mediated by VE-cadherin, integrin-β2, and ICAM-1, stabilize the clusters. Subsequently, EPC sprouting into the stiffer, intact matrix leads to vascular network formation. In vivo examination further corroborated hypoxia-driven clustering of EPCs. Overall, this is the first description of how hypoxia mediates cluster-based vasculogenesis, advancing our understanding toward regulating vascular development as well as postnatal vasculogenesis in regeneration and tumorigenesis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Endothelial Progenitor Cells Protect Human Glomerular Endothelial Cells and Podocytes from Complement- and Cytokine-Mediated Injury.Cells. 2021 Jul 2;10(7):1675. doi: 10.3390/cells10071675. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34359843 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix stiffness regulates arteriovenous differentiation of endothelial progenitor cells during vasculogenesis in nude mice.Cell Prolif. 2019 Mar;52(2):e12557. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12557. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Cell Prolif. 2019. PMID: 30485569 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor-C promotes vasculogenesis, angiogenesis, and collagen constriction in three-dimensional collagen gels.J Vasc Surg. 2005 Apr;41(4):699-707. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2005.01.015. J Vasc Surg. 2005. PMID: 15874936
-
Endothelial progenitor cells for postnatal vasculogenesis.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004 Sep;287(3):C572-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00330.2003. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15308462 Review.
-
VE-cadherin and endothelial adherens junctions: active guardians of vascular integrity.Dev Cell. 2013 Sep 16;26(5):441-54. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2013.08.020. Dev Cell. 2013. PMID: 24044891 Review.
Cited by
-
Endothelial Cell Differentiation and Hemogenic Specification.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2022 Jul 29;12(7):a041164. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a041164. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2022. PMID: 35193895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanical regulation of the early stages of angiogenesis.J R Soc Interface. 2022 Dec;19(197):20220360. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2022.0360. Epub 2022 Dec 7. J R Soc Interface. 2022. PMID: 36475392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Importance of Mechanical Forces for in vitro Endothelial Cell Biology.Front Physiol. 2020 Jun 18;11:684. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00684. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32625119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic Stimulations with Bioengineered Extracellular Matrix-Mimicking Hydrogels for Mechano Cell Reprogramming and Therapy.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Jul;10(21):e2300670. doi: 10.1002/advs.202300670. Epub 2023 Apr 29. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37119518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond classical collagen: basement membrane collagen IV in age-associated lung diseases.Eur Respir Rev. 2025 Jul 23;34(177):240192. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0192-2024. Print 2025 Jul. Eur Respir Rev. 2025. PMID: 40701642 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ferkowicz M. J., Yoder M. C., Blood island formation: Longstanding observations and modern interpretations. Exp. Hematol. 33, 1041–1047 (2005). - PubMed
-
- McGrath K. E., Koniski A. D., Malik J., Palis J., Circulation is established in a stepwise pattern in the mammalian embryo. Blood 101, 1669–1675 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Francis S. E., Goh K. L., Hodivala-Dilke K., Bader B. L., Stark M., Davidson D., Hynes R. O., Central roles of α5β1 integrin and fibronectin in vascular development in mouse embryos and embryoid bodies. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 22, 927–933 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Drake C. J., Fleming P. A., Vasculogenesis in the day 6.5 to 9.5 mouse embryo. Blood 95, 1671–1679 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Ellertsdóttir E., Lenard A., Blum Y., Krudewig A., Herwig L., Affolter M., Belting H.-G., Vascular morphogenesis in the zebrafish embryo. Dev. Biol. 341, 56–65 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

