Sal B targets TAZ to facilitate osteogenesis and reduce adipogenesis through MEK-ERK pathway
- PMID: 30907511
- PMCID: PMC6484321
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.14272
Sal B targets TAZ to facilitate osteogenesis and reduce adipogenesis through MEK-ERK pathway
Abstract
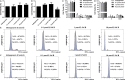
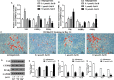
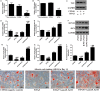
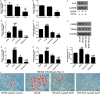
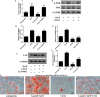
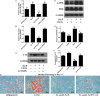
Salvianolic acid B (Sal B), a major bioactive component of Chinese herb, was identified as a mediator for bone metabolism recently. The aim of this study is to investigate the underlying mechanisms by which Sal B regulates osteogenesis and adipogenesis. We used MC3T3-E1 and 3T3-L1 as the study model to explore the changes of cell differentiation induced by Sal B. The results indicated that Sal B at different concentrations had no obvious toxicity effects on cell proliferation during differentiation. Furthermore, Sal B facilitated osteogenesis but inhibited adipogenesis by increasing the expression of transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif (TAZ). Accordingly, TAZ knock-down offset the effects of Sal B on cell differentiation into osteoblasts or adipocytes. Notably, the Sal B induced up-expression of TAZ was blocked by U0126 (the MEK-ERK inhibitor), rather than LY294002 (the PI3K-Akt inhibitor). Moreover, Sal B increased the p-ERK/ERK ratio to regulate the TAZ expression as well as the cell differentiation. In summary, this study suggests for the first time that Sal B targets TAZ to facilitate osteogenesis and reduce adipogenesis by activating MEK-ERK signalling pathway, which provides evidence for Sal B to be used as a potential therapeutic agent for the management of bone diseases.
Keywords: MEK-ERK pathway; Salvianolic acid B; TAZ; adipogenesis; osteogenesis.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that there is no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

