Betahistine for tinnitus
- PMID: 30908589
- PMCID: PMC6433459
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD013093.pub2
Betahistine for tinnitus
Abstract
Background: Tinnitus is a symptom defined as the perception of sound in the absence of an external source. In England alone there are an estimated ¾ million general practice consultations every year where the primary complaint is tinnitus, equating to a major burden on healthcare services. Clinical management strategies include education and advice, relaxation therapy, tinnitus retraining therapy, cognitive behavioural therapy, sound enrichment using ear-level sound generators or hearing aids, and drug therapies to manage co-morbid symptoms such as sleep difficulties, anxiety or depression. As yet, no drug has been approved for tinnitus by a regulatory body. Nonetheless, over 100,000 prescriptions for betahistine are being filled every month in England, and nearly 10% of general practitioners prescribe betahistine for tinnitus.
Objectives: To assess the effects of betahistine in patients with subjective idiopathic tinnitus.
Search methods: The Cochrane ENT Information Specialist searched the Cochrane ENT Register; Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL, via the Cochrane Register of Studies); Ovid MEDLINE; Ovid Embase; Web of Science; ClinicalTrials.gov; ICTRP and additional sources for published and unpublished trials. The date of the search was 23 July 2018.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) recruiting patients of any age with acute or chronic subjective idiopathic tinnitus were included. We included studies where the intervention involved betahistine and this was compared to placebo, no intervention or education and information. We included all courses of betahistine, regardless of dose regimens or formulations and for any duration of treatment.
Data collection and analysis: We used the standard methodological procedures expected by Cochrane. Our primary outcomes included tinnitus loudness and significant adverse effects (upper gastrointestinal discomfort). Our secondary outcomes included tinnitus symptom severity as measured by the global score on a multi-item tinnitus questionnaire, depressive symptoms, symptoms of generalised anxiety, health-related quality of life, other adverse effects (e.g. headache, drowsiness, allergic skin reactions (pruritis, rashes) and exacerbation of tinnitus) and tinnitus intrusiveness. We used GRADE to assess the quality of evidence for each outcome; this is indicated in italics.
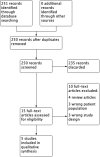
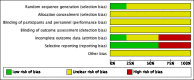
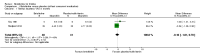
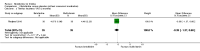
Main results: This review included five studies (with a total of 303 to 305 participants) comparing the effects of betahistine with placebo in adults with subjective idiopathic tinnitus. Four studies were parallel-group RCTs and one had a cross-over design. The risk of bias was unclear in all of the included studies.Due to heterogeneity in the outcomes measured and measurement methods used, very limited data pooling was possible. When we pooled the data from two studies for the primary outcome tinnitus loudness, the mean difference on a 0- to 10-point visual analogue scale at one-month follow-up was not significant between betahistine and placebo (-0.16, 95% confidence interval (CI) -1.01 to 0.70; 81 participants) (very low-quality evidence). There were no reports of upper gastrointestinal discomfort (significant adverse effect) in any study.As a secondary outcome, one study found no difference in the change in the Tinnitus Severity Index between betahistine and placebo (mean difference at 12 weeks 0.02, 95% CI -1.05 to 1.09; 50 participants) (moderate-quality evidence). None of the studies reported the other secondary outcomes of changes in depressive symptoms or depression, anxiety symptoms or generalised anxiety, or health-related quality of life as measured by a validated instrument, nor tinnitus intrusiveness.Other adverse effects that were reported were not treatment-related.
Authors' conclusions: There is an absence of evidence to suggest that betahistine has an effect on subjective idiopathic tinnitus when compared to placebo. The evidence suggests that betahistine is generally well tolerated with a similar risk of adverse effects to placebo treatments. The quality of evidence for the reported outcomes, using GRADE, ranged from moderate to very low.If future research into the effectiveness of betahistine in patients with tinnitus is felt to be warranted, it should use rigorous methodology. Randomisation and blinding should be of the highest quality, given the subjective nature of tinnitus and the strong likelihood of a placebo response. The CONSORT statement should be used in the design and reporting of future studies. We also recommend the development of validated, patient-centred outcome measures for research in the field of tinnitus.
Conflict of interest statement
Deborah A Hall: is an NIHR Senior Investigator and Section Editor for the journal
Inge Wegner: none known.
Adriana L Smit: none known.
Don McFerran: receives royalties for writing books on tinnitus has received consultancy honoraria from GlaxoSmithKline, Autifony and Otonomy.
Inge Stegeman: none known.
Figures












Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013093
References
References to studies included in this review
Cekkayan 1996 {published data only}
-
- Cekkayan S, Ozlüoğlu L, Yoloğlu S, Söylemezoğlu S, Erpek G. Comparison of the efficiency of betahistine hydrochloride and gingko biloba extract in tinnitus patients [Tinnituslu hastalarda betahistin ve gingko biloba ekstresinin etkinliginin karsilastirilmasi]. K.B.B. ve Baş Boyun Cerrahisi Dergisi 1996;4:19‐22.
Kay 1981 {published data only}
-
- Kay NJ. Oral chemotherapy for tinnitus. British Journal of Audiology 1981;15(2):123‐4. [PUBMED: 7225648] - PubMed
Ma 2006 {published data only}
-
- Ma F, Xin Y, Zhao YM, Lü JQ. Efficacy of betahistine mesilate combined with flunarizine hydrochloride for treating tinnitus [倍他司汀联合盐酸氟桂利嗪治疗耳鸣的随机双盲对照初步研究]. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2006;41(4):269‐73. [PUBMED: 16848175] - PubMed
Maqbool 2010 {published data only}
-
- Maqbool S, Ahmed B, Manzoor T. Eifficacy of betahistine hydrocholride in tinnitus due to noise‐induced hearing loss. Pakistan Armed Forces Medical Journal 2010; Vol. 60, issue 1.
Mashali 2016 {published data only}
-
- Mashali L, Rahimi S, Rekabi H, Rahimi P. The comparative study of two drugs of carbamazepine and betahistine on tinnitus improvement. International Journal of Pharmacy & Technology 2016;8(3):14774‐81.
References to studies excluded from this review
de Kernier 2000 {published data only}
-
- Kernier C. Vertigo and tinnitus [Vertiges et acouphenes]. Actualites Pharmaceutiques 2000;382:47‐50.
Jakobs 1978 {published data only}
-
- Jakobs P, Martin G. The therapy of tinnitus resulting from blast injury [Die Therapie des Tinnitus nach knalltraumatischer Schädigung]. HNO 1978;26(3):104‐6. [PUBMED: 346541] - PubMed
Kluyskens 1990 {published data only}
-
- Kluyskens P, Lambert P, D'Hooge D. Trimetazidine versus betahistine in vestibular vertigo. A double blind study [Trimétazidine contre bétahistine dans les vertiges vestibulaires. Etude en double aveugle]. Annales d'Oto‐laryngologie et de Chirurgie Cervico Faciale 1990;107(1):11‐9. [PUBMED: 2240994] - PubMed
Larikova 2005 {published data only}
-
- Larikova TI, Cherevikova GM. Betaserc and improvement of life quality in war veterans. Zhurnal Nevrologii i Psikhiatrii Imeni S.S. Korsakova 2005;105(3):68‐70. [PUBMED: 15822746] - PubMed
Oosterveld 1984 {published data only}
-
- Oosterveld WJ. Betahistine dihydrochloride in the treatment of vertigo of peripheral vestibular origin. A double‐blind placebo‐controlled study. Journal of Laryngology and Otology 1984;98(1):37‐41. [PUBMED: 6363584] - PubMed
Robson 1994 {published data only}
-
- Robson AK, Birchall JP. Management of tinnitus. Prescribers' Journal 1994;34(1):1‐7.
Singarelli 1979 {published data only}
-
- Singarelli S. Double‐blind trial on the efficacy of betahistine hydrochloride in a group of outpatients with positional vertigo and tinnitus [Studio in doppio cieco sull'efficacia del cloridato di betaistina nel trattamento ambulatoriale di un gruppo di pazienti affetti da vertigine di posizione e acufeni]. Nuovo Archivio Italiano di Otologia, Rinologia e Laringologia 1979;7:69‐72.
Sirimanna 1992 {published data only}
-
- Sirimanna T, Stephens D. Coping with tinnitus. Practitioner 1992;236(1518):821‐6. [PUBMED: 1461881] - PubMed
Sonmez 2013 {published data only}
-
- Sönmez O, Külahlı I, Vural A, Sahin MI, Aydın M. The evaluation of ozone and betahistine in the treatment of tinnitus. European Archives of Oto‐rhino‐laryngology 2013;270(7):1999‐2006. [PUBMED: 23100082] - PubMed
Werkman 1982 {published data only}
-
- Werkman BK. The treatment of tinnitus. Clinical Otolaryngology and Allied Sciences 1982;7(5):354. - PubMed
Additional references
Adjamian 2009
-
- Adjamian P, Sereda M, Hall DA. The mechanisms of tinnitus: perspectives from human functional neuroimaging. Hearing Research 2009;253(1‐2):15‐31. [PUBMED: 19364527] - PubMed
Baguley 2013
-
- Baguley D, McFerran D, Hall D. Tinnitus. Lancet 2013;382(9904):1600‐7. [PUBMED: 23827090] - PubMed
Barak 2008
-
- Barak N. Betahistine: what’s new on the agenda?. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs 2008;17:795–804. - PubMed
Beck 1988
-
- Beck AT, Steer RA, Garbin MG. Psychometric properties of the Beck Depression Inventory: twenty‐five years of evaluation. Clinical Psychology Review 1988;8(1):77‐100. [DOI: ]
Beck 1988a
-
- Beck AT, Epstein N, Brown G, Steer RA. An inventory for measuring clinical anxiety: psychometric properties. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1988;56(6):893‐7. [PUBMED: 3204199] - PubMed
Beck 1996
-
- Beck AT, Steer RA, Brown GK. Manual for the Beck Depression Inventory‐II. San Antonio, Texas: Psychological Corporation, 1996.
Biesinger 2011
-
- Biesinger E, Bo L, Ridder D, Goodey R, Herraiz C, Kleinjung T, et al. Algorithm for the diagnostic & therapeutic management of tinnitus. http://www.tinnitusresearch.org/images/files/migrated/TRI_Tinnitus_Flowc... (accessed 21 May 2018) 2011.
Buss 1998
-
- Buss E, Hall JW 3rd, Grose JH, Hatch DR. Perceptual consequences of peripheral hearing loss: do edge effects exist for abrupt cochlear lesions?. Hearing Research 1998;125(1‐2):98‐108. [PUBMED: 9833964] - PubMed
Cima 2012
-
- Cima RF, Maes IH, Joore MA, Scheyen DJ, Refaie A, Baguley DM, et al. Specialised treatment based on cognitive behaviour therapy versus usual care for tinnitus: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2012;379(9830):1951‐9. [PUBMED: 22633033] - PubMed
Coelho 2016
-
- Coelho C, Tyler R, Ji H, Rojas‐Roncancio E, Witt S, Tao P, et al. Survey on the effectiveness of dietary supplements to treat tinnitus. American Journal of Audiology 2016;25(3):184‐205. [PUBMED: 27681261] - PubMed
CONSORT 2010
Department of Health 2009
-
- Department of Health. Provision of Services for Adults with Tinnitus. A Good Practice Guide. London: Central Office of Information, 2009.
Dietrich 2001
-
- Dietrich V, Nieschalk M, Stoll W, Rajan R, Pantev C. Cortical reorganization in patients with high frequency cochlear hearing loss. Hearing Research 2001;158(1‐2):95‐101. [PUBMED: 11506941] - PubMed
Dobie 1999
-
- Dobie RA. A review of randomized clinical trials in tinnitus. Laryngoscope 1999;109(8):1202‐11. [PUBMED: 10443820] - PubMed
Dong 2010
-
- Dong S, Rodger J, Mulders WH, Robertson D. Tonotopic changes in GABA receptor expression in guinea pig inferior colliculus after partial unilateral hearing loss. Brain Research 2010;1342:24‐32. [PUBMED: 20438718] - PubMed
Dziadziola 1999
-
- Dziadziola JK, Laurikainen EL, Rachel JD, Quirk WS. Betahistine increases vestibular blood flow. Otolaryngology ‐ Head and Neck Surgery 1999;120(3):400‐5. [PUBMED: 10064646] - PubMed
Eggermont 2004
-
- Eggermont JJ, Roberts LE. The neuroscience of tinnitus. Trends in Neurosciences 2004;27(11):676‐82. [PUBMED: 15474168] - PubMed
El‐Shunnar 2011
Electronic Medicines Compendium 2015
-
- Electronic Medicines Compendium. Betahistine dihydrochloride 16 mg tablets. https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/medicine/26617 2015.
Engineer 2011
Folmer 2000
-
- Folmer RL. Managing chronic tinnitus as phantom auditory pain. Audiology Online. Available at https://www.audiologyonline.com/articles/managing‐chronic‐tinnitus‐as‐ph... 2000 (accessed 29 September 2018).
Fowler 1944
-
- Fowler E. Head noises in normal and in disordered ears: significance, measurement, differentiation and treatment. Archives of Otolaryngology 1944;39(6):498‐503.
Fuller 2017
Furlong 2001
-
- Furlong WJ, Feeny DH, Torrance GW, Barr RD. The Health Utilities Index (HUI) system for assessing health‐related quality of life in clinical studies. Annals of Medicine 2001;33(5):375‐84. [PUBMED: 11491197] - PubMed
Gallus 2015
-
- Gallus S, Lugo A, Garavello W, Bosetti C, Santoro E, Colombo P, et al. Prevalence and determinants of tinnitus in the Italian adult population. Neuroepidemiology 2015;45(1):12‐9. [PUBMED: 26182874] - PubMed
Guitton 2003
Hall 2011
Hall 2017
-
- Hall DA, Mehta RL, Fackrell K. How to choose between measures of tinnitus loudness for clinical research? A report on the reliability and validity of an investigator‐administered test and a patient‐reported measure using baseline data collected in a phase IIa drug trial. American Journal of Audiology 2017;26(3):338‐46. [PUBMED: 28841725] - PubMed
Hall 2018a
Hall 2018b
-
- Hall DA, Smith H, Hibbert A, Colley V, Haider HF, Horobin A, et al. The COMiT'ID study: developing core outcome domains sets for clinical trials of sound‐, psychology‐, and pharmacology‐based interventions for chronic subjective tinnitus in adults. Trends in Hearing 2018;22:2331216518814384. [PUBMED: 30488765] - PMC - PubMed
Hallam 2009
-
- Hallam RS. TQ, Manual of the Tinnitus Questionnaire: Revised and Updated. 2nd Edition. London: Polpresa Press, 2009.
Hamilton 1960
Han 2009
Handbook 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hays 1993
-
- Hays RD, Sherbourne CD, Mazel RM. The RAND 36‐Item Health Survey 1.0. Health Economics 1993;2(3):217‐27. [PUBMED: 8275167] - PubMed
Henry 2005
-
- Henry JA, Dennis KC, Schechter MA. General review of tinnitus: prevalence, mechanisms, effects, and management. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research 2005;48(5):1204‐35. [PUBMED: 16411806] - PubMed
Henry 2008
Hiller 2006
-
- Hiller W, Goebel G. Factors influencing tinnitus loudness and annoyance. Archives of Otolaryngology‐‐Head & Neck Surgery 2006;132(12):1323‐30. [PUBMED: 17178943] - PubMed
Hoare 2011
Hoare 2014
James 2001
Jastreboff 1988
-
- Jastreboff PJ, Brennan JF, Coleman JK, Sasaki CT. Phantom auditory sensation in rats: an animal model for tinnitus. Behavioral Neuroscience 1988;102(6):811‐22. [PUBMED: 3214530] - PubMed
Jastreboff 1990
-
- Jastreboff PJ. Phantom auditory perception (tinnitus): mechanisms of generation and perception. Neuroscience Research 1990;8(4):221‐54. [PUBMED: 2175858] - PubMed
Jastreboff 2004
-
- Jastreboff PJ, Hazell JWP. Tinnitus Retraining Therapy. Cambridge University Press, 2004. [DOI: ]
Jeck‐Thole 2006
-
- Jeck‐Thole S, Wagner W. Betahistine: a retrospective synopsis of safety data. Drug Safety 2006;29(11):1049‐59. [PUBMED: 17061910] - PubMed
Kluk 2006
-
- Kluk K, Moore BC. Dead regions in the cochlea and enhancement of frequency discrimination: effects of audiogram slope, unilateral versus bilateral loss, and hearing‐aid use. Hearing Research 2006;222(1‐2):1‐15. [PUBMED: 17071031] - PubMed
Kuk 1990
-
- Kuk FK, Tyler RS, Russell D, Jordan H. The psychometric properties of a tinnitus handicap questionnaire. Ear and Hearing 1990;11(6):434‐45. [PUBMED: 2073977] - PubMed
König 2006
-
- König O, Schaette R, Kempter R, Gross M. Course of hearing loss and occurrence of tinnitus. Hearing Research 2006;221(1‐2):59‐64. [PUBMED: 16962270] - PubMed
Lacour 2007
Laurikainen 1993
-
- Laurikainen EA, Miller JM, Quirk WS, Kallinen J, Ren T, Nuttall AL, et al. Betahistine induced vascular effects in the rat cochlea. American Journal of Otology 1993;14(1):24‐30. [PUBMED: 8424471] - PubMed
Martines 2010
Martinez 1972
-
- Martinez DM. The effect of Serc (betahistine hydrochloride) on the circulation of the inner ear in experimental animals. Acta Oto‐laryngologica. Supplementum 1972;305:29‐47. [PUBMED: 4353749] - PubMed
McCormack 2016
-
- McCormack A, Edmondson‐Jones M, Somerset S, Hall DA. A systematic review of the reporting of tinnitus prevalence and severity. Hearing Research 2016;337:70‐9. [PUBMED: 27246985] - PubMed
McDermott 1998
-
- McDermott HJ, Lech M, Kornblum MS, Irvine DR. Loudness perception and frequency discrimination in subjects with steeply sloping hearing loss: possible correlates of neural plasticity. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 1998;104(4):2314‐25. [PUBMED: 10491696] - PubMed
McFerran 2018
Meikle 2012
-
- Meikle MB, Henry JA, Griest SE, Stewart BJ, Abrams HB, McArdle R, et al. The tinnitus functional index: development of a new clinical measure for chronic, intrusive tinnitus. Ear and Hearing 2012;33(2):153‐76. [PUBMED: 22156949] - PubMed
Melcher 2013
-
- Melcher JR, Knudson IM, Levine RA. Subcallosal brain structure: correlation with hearing threshold at supra‐clinical frequencies (>8 kHz), but not with tinnitus. Hearing Research 2013;295:79‐86. [PUBMED: 22504034] - PubMed
Middleton 2011
-
- Middleton JW, Kiritani T, Pedersen C, Turner JG, Shepherd GM, Tzounopoulos T. Mice with behavioral evidence of tinnitus exhibit dorsal cochlear nucleus hyperactivity because of decreased GABAergic inhibition. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2011;108(18):7601‐6. [PUBMED: 21502491] - PMC - PubMed
Moller 2000
-
- Moller AR. Similarities between severe tinnitus and chronic pain. Journal of the American Academy of Audiology 2000;11(3):115‐24. [PUBMED: 10755808] - PubMed
Moore 2009
-
- Moore BC, Vinay SN. Enhanced discrimination of low‐frequency sounds for subjects with high‐frequency dead regions. Brain 2009;132(Pt 2):524‐36. [PUBMED: 19036764] - PubMed
Mulders 2010
Murdin 2016
Mühlnickel 1998
Newman 1996
-
- Newman CW, Jacobson GP, Spitzer JB. Development of the Tinnitus Handicap Inventory. Archives of Otolaryngology‐‐Head & Neck Surgery 1996;122(2):143‐8. [PUBMED: 8630207] - PubMed
Noreña 2005
Noreña 2011
-
- Noreña AJ. An integrative model of tinnitus based on a central gain controlling neural sensitivity. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews 2011;35(5):1089‐109. [PUBMED: 21094182] - PubMed
Pathy 1977
-
- Pathy J, Menon G, Reynolds A, Strik R. Betahistine hydrochloride (Serc) in cerebrovascular disease a placebo‐controlled study. Age and Ageing 1977;6(3):179‐84. - PubMed
Phillips 2008
Pilati 2012
Ratnayake 2009
-
- Ratnayake SA, Jayarajan V, Bartlett J. Could an underlying hearing loss be a significant factor in the handicap caused by tinnitus?. Noise & Health 2009;11(44):156‐60. [PUBMED: 19602769] - PubMed
Rauschecker 1999
-
- Rauschecker JP. Auditory cortical plasticity: a comparison with other sensory systems. Trends in Neurosciences 1999;22(2):74‐80. [PUBMED: 10092047] - PubMed
Rauschecker 2010
Reiss 1986
-
- Reiss S, Peterson RA, Gursky DM, McNally RJ. Anxiety sensitivity, anxiety frequency and the prediction of fearfulness. Behaviour Research and Therapy 1986;24(1):1‐8. [PUBMED: 3947307] - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Roberts 2010
Sahley 2001
-
- Sahley TL, Nodar RH. A biochemical model of peripheral tinnitus. Hearing Research 2001;152(1‐2):43‐54. [PUBMED: 11223280] - PubMed
Sanchez 2002
-
- Sanchez TG, Ferrari GMS. The control of tinnitus through hearing aids: suggestions for optimal use. Pró‐Fono Revista de Atualização Científica 2002;14:111‐8.
Schaette 2006
-
- Schaette R, Kempter R. Development of tinnitus‐related neuronal hyperactivity through homeostatic plasticity after hearing loss: a computational model. European Journal of Neuroscience 2006;23(11):3124‐38. [PUBMED: 16820003] - PubMed
Schaette 2011
Seki 2003
-
- Seki S, Eggermont JJ. Changes in spontaneous firing rate and neural synchrony in cat primary auditory cortex after localized tone‐induced hearing loss. Hearing Research 2003;180(1‐2):28‐38. [PUBMED: 12782350] - PubMed
Sereda 2011
Sereda 2015
Skevington 2004
-
- Skevington SM, Lotfy M, O'Connell KA. The World Health Organization's WHOQOL‐BREF quality of life assessment: psychometric properties and results of the international field trial. A report from the WHOQOL group. Quality of Life Research 2004;13(2):299‐310. [PUBMED: 15085902] - PubMed
Sweetow 1990
-
- Sweetow RW, Levy MC. Tinnitus severity scaling for diagnostic/therapeutic usage. Hearing Instruments 1990;41(20‐1):46.
Tass 2012
-
- Tass PA, Adamchic I, Freund HJ, Stackelberg T, Hauptmann C. Counteracting tinnitus by acoustic coordinated reset neuromodulation. Restorative Neurology and Neuroscience 2012;30(2):137‐59. [PUBMED: 22414611] - PubMed
Thai‐Van 2002
-
- Thai‐Van H, Micheyl C, Norena A, Collet L. Local improvement in auditory frequency discrimination is associated with hearing‐loss slope in subjects with cochlear damage. Brain 2002;125(Pt 3):524‐37. [PUBMED: 11872610] - PubMed
Thai‐Van 2003
-
- Thai‐Van H, Micheyl C, Moore BC, Collet L. Enhanced frequency discrimination near the hearing loss cut‐off: a consequence of central auditory plasticity induced by cochlear damage?. Brain 2003;126(Pt 10):2235‐45. [PUBMED: 12847078] - PubMed
Timmerman 1994
-
- Timmerman H. Pharmacotherapy of vertigo: any news to be expected?. Acta Oto‐laryngologica. Supplementum 1994;513:28‐32. [PUBMED: 7910713] - PubMed
Tunis 2016
Tunkel 2014
-
- Tunkel DE, Bauer CA, Sun GH, Rosenfeld RM, Chandrasekhar SS, Cunningham ER Jr, et al. Clinical practice guideline: tinnitus executive summary. Otolaryngology‐‐Head and Neck Surgery 2014;151(4):533‐41. [PUBMED: 25274374] - PubMed
Unemoto 1982
-
- Unemoto H, Sasa M, Takaori S, Ito J, Matsuoka I. Inhibitory effect of betahistine on polysynaptic neurons in the lateral vestibular nucleus. Archives of Oto‐rhino‐laryngology 1982;236(3):229‐36. [PUBMED: 7159275] - PubMed
van Esch 2018
-
- Esch B, Zaag‐Loonen HJ, Bruintjes T, Murdin L, James A, Benthem PP. Betahistine for Ménière's disease or syndrome. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2018, Issue 1. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012914] - DOI
Vanneste 2012
Weisz 2005
Wilson 1991
-
- Wilson PH, Henry J, Bowen M, Haralambous G. Tinnitus reaction questionnaire: psychometric properties of a measure of distress associated with tinnitus. Journal of Speech and Hearing Research 1991;34(1):197‐201. [PUBMED: 2008074] - PubMed
Zigmond 1983
-
- Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1983;67(6):361‐70. [PUBMED: 6880820] - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

