Application of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles to Improve the Efficiency of Anticancer Drugs
- PMID: 30909401
- PMCID: PMC6474076
- DOI: 10.3390/nano9030474
Application of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles to Improve the Efficiency of Anticancer Drugs
Abstract
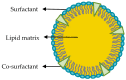
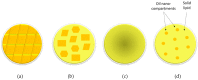
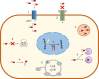
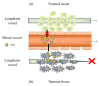
Drug delivery systems have opened new avenues to improve the therapeutic effects of already-efficient molecules. Particularly, Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs) have emerged as promising nanocarriers in cancer therapy. SLNs offer remarkable advantages such as low toxicity, high bioavailability of drugs, versatility of incorporation of hydrophilic and lipophilic drugs, and feasibility of large-scale production. Their molecular structure is crucial to obtain high quality SLN preparations and it is determined by the relationship between the composition and preparation method. Additionally, SLNs allow overcoming several physiological barriers that hinder drug delivery to tumors and are also able to escape multidrug resistance mechanisms, characteristic of cancer cells. Focusing on cell delivery, SLNs can improve drug delivery to target cells by different mechanisms, such as passive mechanisms that take advantage of the tumor microenvironment, active mechanisms by surface modification of SLNs, and codelivery mechanisms. SLNs can incorporate many different drugs and have proven to be effective in different types of tumors (i.e., breast, lung, colon, liver, and brain), corroborating their potential. Finally, it has to be taken into account that there are still some challenges to face in the application of SLNs in anticancer treatments but their possibilities seem to be high.
Keywords: cancer; chemotherapy; drug delivery; solid lipid nanoparticles; tumor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Limeres M.J., Moretton M.A., Bernabeu E., Chiappetta D.A., Cuestas M.L. Thinking small, doing big: Current success and future trends in drug delivery systems for improving cancer therapy with special focus on liver cancer. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019;95:328–341. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2018.11.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Prasad P.V., Shrivastav T.G. Nanotechnological contribution to drug delivery system: A reappraisal. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2014;5:194–199. doi: 10.4236/jbnb.2014.53023. - DOI
-
- Kumar N., Kumar R. Nanotechnology and Nanomaterials in the Treatment of Life-threatening Diseases. William Andrew; Waltham, MA, USA: 2013.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

