Isolated adrenocorticotropic hormone deficiency and thyroiditis associated with nivolumab therapy in a patient with advanced lung adenocarcinoma: a case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 30909965
- PMCID: PMC6434613
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-019-2002-2
Isolated adrenocorticotropic hormone deficiency and thyroiditis associated with nivolumab therapy in a patient with advanced lung adenocarcinoma: a case report and review of the literature
Abstract
Introduction: Immune checkpoint inhibitors are a promising class of anticancer drugs. The clinical benefits afforded by immune checkpoint inhibitors can be accompanied by immune-related adverse events that affect multiple organs, and endocrine immune-related adverse events include thyroiditis and hypophysitis. Hypophysitis is less frequent and has a less severe clinical presentation in patients treated with other immune checkpoint inhibitors, such as nivolumab, pembrolizumab, and atezolizumab, than in those treated with ipilimumab. However, studies have described isolated adrenocorticotropic hormone deficiency cases associated with nivolumab, pembrolizumab, and atezolizumab therapy, most of which occurred during the course of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. We report a rare case of patient with isolated adrenocorticotropic hormone deficiency that occurred after nivolumab therapy.
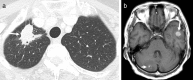
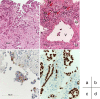
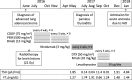
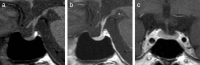
Case presentation: A 69-year-old Japanese woman with advanced lung adenocarcinoma developed painless thyroiditis with transient elevations of serum thyroid hormones during 3 months of cancer treatment with nivolumab and began thyroid hormone replacement therapy for subsequent primary hypothyroidism. Four months after nivolumab therapy was discontinued, she developed isolated adrenocorticotropic hormone deficiency; corticosteroid replacement therapy relieved her secondary adrenal insufficiency symptoms, such as anorexia and fatigue. Human leukocyte antigen typing revealed the presence of DRB1*04:05-DQB1*04:01-DQA1*03:03 and DRB1*09:01-DQB1*03:03-DQA1*03:02 haplotypes, which increase susceptibility to autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome associated with thyroid and pituitary disorders in the Japanese population.
Conclusions: Our patient developed thyroiditis during cancer treatment with nivolumab and subsequently exhibited isolated adrenocorticotropic hormone deficiency 4 months after discontinuing the drug. Administration of nivolumab in combination with a genetic predisposition to polyglandular autoimmunity probably caused both the thyroiditis and hypophysitis, resulting in primary hypothyroidism and isolated adrenocorticotropic hormone deficiency, respectively, in our patient. The present case highlights the need for physicians to be aware that endocrine immune-related adverse events, including hypophysitis, can occur more than several months after discontinuing a drug.
Keywords: Human leukocyte antigen; Hydrocortisone; Isolated adrenocorticotropic hormone deficiency; Lung adenocarcinoma; Nivolumab; Thyroiditis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Michot JM, Bigenwald C, Champiat S, Collins M, Carbonnel F, Postel-Vinay S, Berdelou A, Varga A, Bahleda R, Hollebecque A, Massard C, Fuerea A, Ribrag V, Gazzah A, Armand JP, Amellal N, Angevin E, Noel N, Boutros C, Mateus C, Robert C, Soria JC, Marabelle A, Lambotte O. Immune-related adverse events with immune checkpoint blockade: a comprehensive review. Eur J Cancer. 2016;54:139–148. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2015.11.016. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barroso-Sousa R, Barry WT, Garrido-Castro AC, Hodi FS, Min L, Krop IE, Tolaney SM. Incidence of endocrine dysfunction following the use of different immune checkpoint inhibitor regimens: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4:173–182. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.3064. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

