Effectiveness of a Novel Nutraceutical Compound Containing Red Yeast Rice, Polymethoxyflavones and Antioxidants in the Modulation of Cholesterol Levels in Subjects With Hypercholesterolemia and Low-Moderate Cardiovascular Risk: The NIRVANA Study
- PMID: 30914970
- PMCID: PMC6421317
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00217
Effectiveness of a Novel Nutraceutical Compound Containing Red Yeast Rice, Polymethoxyflavones and Antioxidants in the Modulation of Cholesterol Levels in Subjects With Hypercholesterolemia and Low-Moderate Cardiovascular Risk: The NIRVANA Study
Abstract
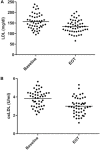
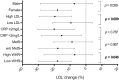
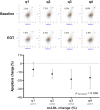
Background: Red yeast rice supplements are broadly accepted as treatment for dyslipidaemia in subjects without high cardiovascular (CV) risk. Their effect on lipid profile is well known, but few data are available on their effect on endothelial function. Objectives: To study the effect of a novel nutraceutical compound (NC) containing low monacolin K dose, polymethoxyflavones and antioxidants on lipid profile, endothelial function and oxidative stress. Methods: Fifty-two subjects with low-moderate CV risk and dyslipidaemia (according to European guidelines) were enrolled and treated for 8 weeks with the NC. Blood samples were collected at baseline and at the end of treatment to assess changes in lipid profile, endothelial function and oxidative stress. The primary endpoint was the reduction of low density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. Endothelial function was assessed through measurement of rate of apoptosis and nitric oxide (NO) production in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) treated with subject's serum. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein, 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE) and oxidized LDL (oxLDL) were markers of oxidative stress. Results: Fifty subjects completed the study. The treatment caused a significant decrease in LDL (-15.6%, p < 0.001), oxLDL (-21.5%, p < 0.001), total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides, and ApoB. Apoptosis rate of HUVECs significantly decreased (-15.9%, p < 0.001). No changes were noted for NO levels and 4-HNE protein adducts. The reduction of the apoptosis rate was correlated to the reduction of oxLDL. Conclusion: An 8-week treatment based on a novel NC containing low manocolin K dose, polymethoxyflavones and antioxidants improved lipid profile in subjects with dyslipidaemia and low-moderate CV risk. Secondarily, we observed an improvement in surrogate markers of endothelial function that may result from the reduction of oxLDL (Registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov, NCT03216811).
Keywords: cardiovascular prevention; endothelial function; hypercholesterolemia; nutraceutical compound; red yeast rice.
Figures

References
-
- Affuso F., Ruvolo A., Micillo F., Saccà L., Fazio S. (2010). Effects of a nutraceutical combination (berberine, red yeast rice and policosanols) on lipid levels and endothelial function randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 20 656–661. 10.1016/j.numecd.2009.05.017 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alberti K. G., Eckel R. H., Grundy S. M., Zimmet P. Z., Cleeman J. I., Donato K. A., et al. (2009). Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the international diabetes federation task force on epidemiology and prevention; national heart, lung, and blood institute; American heart association; world heart federation; international. Circulation 120 1640–1645. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.192644 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barrios V., Escobar C., Cicero A. F. G., Burke D., Fasching P., Banach M., et al. (2017). A nutraceutical approach (Armolipid Plus) to reduce total and LDL cholesterol in individuals with mild to moderate dyslipidemia: review of the clinical evidence. Atheroscler. Suppl. 24 1–15. 10.1016/j.atherosclerosissup.2016.10.003 - DOI - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

