Dysregulation of CRMP2 Post-Translational Modifications Drive Its Pathological Functions
- PMID: 30915713
- PMCID: PMC6728212
- DOI: 10.1007/s12035-019-1568-4
Dysregulation of CRMP2 Post-Translational Modifications Drive Its Pathological Functions
Abstract
Collapsin response mediator proteins (CRMPs) are a family of ubiquitously expressed, homologous phosphoproteins best known for coordinating cytoskeletal formation and regulating cellular division, migration, polarity, and synaptic connection. CRMP2, the most studied of the five family members, is best known for its affinity for tubulin heterodimers and function in regulating the microtubule network. These functions are tightly regulated by post-translational modifications including phosphorylation, SUMOylation, oxidation, and O-GlcNAcylation. While CRMP2's physiological functions rely mostly on its non-phosphorylated state, dysregulation of CRMP2 phosphorylation and SUMOylation has been reported to be involved in the pathophysiology of multiple diseases including cancer, chronic pain, spinal cord injury, neurofibromatosis type 1, and others. Here, we provide a consolidated update on what is known about CRMP2 signaling and function, first focusing on axonal growth and neuronal polarity, then illustrating the link between dysregulated CRMP2 post-translational modifications and diseases. We additionally discuss the roles of CRMP2 in non-neuronal cells, both in the CNS and regions of the periphery. Finally, we offer thoughts on the therapeutic implications of modulating CRMP2 function in a variety of diseases.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; CRMP2; Cancer; Chronic pain; Human disease; Interactome; Multiple sclerosis; Neurite outgrowth; Non-neuronal cells; Post-translational modifications; Stroke; Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
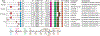
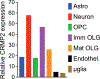
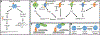

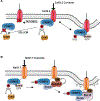
References
-
- Makihara H, Nakai S, Ohkubo W, Yamashita N, Nakamura F, Kiyonari H, Shioi G, Jitsuki-Takahashi A, Nakamura H, Tanaka F, Akase T, Kolattukudy P, Goshima Y (2016) CRMP1 and CRMP2 have synergistic but distinct roles in dendritic development. Genes to cells : devoted to molecular & cellular mechanisms 21 (9):994–1005. doi:10.1111/gtc.12399 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

