Overall Survival with Fulvestrant plus Anastrozole in Metastatic Breast Cancer
- PMID: 30917258
- PMCID: PMC6885383
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1811714
Overall Survival with Fulvestrant plus Anastrozole in Metastatic Breast Cancer
Erratum in
-
Overall Survival with Fulvestrant plus Anastrozole in Metastatic Breast Cancer.N Engl J Med. 2019 Jun 6;380(23):2282. doi: 10.1056/NEJMx190018. N Engl J Med. 2019. PMID: 31167077 No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: We previously reported prolonged progression-free survival and marginally prolonged overall survival among postmenopausal patients with hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer who had been randomly assigned to receive the aromatase inhibitor anastrozole plus the selective estrogen-receptor down-regulator fulvestrant, as compared with anastrozole alone, as first-line therapy. We now report final survival outcomes.
Methods: We randomly assigned patients to receive either anastrozole or fulvestrant plus anastrozole. Randomization was stratified according to adjuvant tamoxifen use. Analysis of survival was performed by means of two-sided stratified log-rank tests and Cox regression. Efficacy and safety were compared between the two groups, both overall and in subgroups.
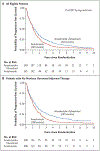
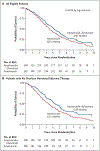
Results: Of 707 patients who had undergone randomization, 694 had data available for analysis. The combination-therapy group had 247 deaths among 349 women (71%) and a median overall survival of 49.8 months, as compared with 261 deaths among 345 women (76%) and a median overall survival of 42.0 months in the anastrozole-alone group, a significant difference (hazard ratio for death, 0.82; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.69 to 0.98; P = 0.03 by the log-rank test). In a subgroup analysis of the two strata, overall survival among women who had not received tamoxifen previously was longer with the combination therapy than with anastrozole alone (median, 52.2 months and 40.3 months, respectively; hazard ratio, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.58 to 0.92); among women who had received tamoxifen previously, overall survival was similar in the two groups (median, 48.2 months and 43.5 months, respectively; hazard ratio, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.74 to 1.27) (P = 0.09 for interaction). The incidence of long-term toxic effects of grade 3 to 5 was similar in the two groups. Approximately 45% of the patients in the anastrozole-alone group crossed over to receive fulvestrant.
Conclusions: The addition of fulvestrant to anastrozole was associated with increased long-term survival as compared with anastrozole alone, despite substantial crossover to fulvestrant after progression during therapy with anastrozole alone. The results suggest that the benefit was particularly notable in patients without previous exposure to adjuvant endocrine therapy. (Funded by the National Cancer Institute and AstraZeneca; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT00075764.).
Copyright © 2019 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures
Comment in
-
Fulvestrant enables better outcomes.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2019 Jun;16(6):337. doi: 10.1038/s41571-019-0211-7. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30967645 No abstract available.
References
-
- Di Leo A, Jerusalem G, Petruzelka L, et al. Results of the CONFIRM phase III trial comparing fulvestrant 250 mg with fulvestrant 500 mg in postmenopausal women with estrogen receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 4594–600. - PubMed
-
- Bergh J, Jönsson PE, Lidbrink EK, et al. FACT: an open-label randomized phase III study of fulvestrant and anastrozole in combination compared with anastrozole alone as first-line therapy for patients with receptor-positive postmenopausal breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 1919–25. - PubMed
-
- Johnston SR, Kilburn LS, Ellis P, et al. Fulvestrant plus anastrozole or placebo versus exemestane alone after progression on non-steroidal aromatase inhibitors in postmenopausal patients with hormone-receptor-positive locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer (SoFEA): a composite, multicentre, phase 3 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol 2013; 14: 989–98. - PubMed
-
- Di Leo A, Jerusalem G, Torres R, et al. First-line vs second-line fulvestrant for hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer: a post-hoc analysis of the CONFIRM study. Breast 2018; 38: 144–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- UG1 CA233329/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA013612/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA013612/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180801/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233160/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA180888, CA180819, CA180863, CA189808, CA180801,/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180888/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA13612/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180858/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189952/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046282/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180863/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA062203/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189808/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180819/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189953/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233328/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
