Population Pharmacokinetics with Monte Carlo Simulations of Gentamicin in a Population of Severely Ill Adult Patients from Sub-Saharan Africa
- PMID: 30917981
- PMCID: PMC6437512
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02328-18
Population Pharmacokinetics with Monte Carlo Simulations of Gentamicin in a Population of Severely Ill Adult Patients from Sub-Saharan Africa
Abstract
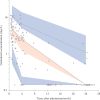
In sub-Saharan Africa (SSA), gentamicin is commonly used for severe infections in non-intensive-care-unit (ICU) settings, but pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic data for this specific population are lacking. We performed a population pharmacokinetic study in an adult Mozambican non-ICU hospital population treated with gentamicin (n = 48) and developed a pharmacokinetic model using nonlinear mixed-effects modeling. Simulations showed that non-ICU patient populations in SSA may be at substantial risk for underexposure to gentamicin during routine once-daily dosing.
Keywords: aminoglycosides; gentamicin; pharmacodynamics; population pharmacokinetics; severe illness; sub-Saharan Africa.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

References
-
- Ford N, Shubber Z, Meintjes G, Grinsztejn B, Eholie S, Mills EJ, Davies MA, Vitoria M, Penazzato M, Nsanzimana S, Frigati L, O'Brien D, Ellman T, Ajose O, Calmy A, Doherty M. 2015. Causes of hospital admission among people living with HIV worldwide: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet HIV 2:e438–e444. doi:10.1016/S2352-3018(15)00137-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Meintjes G, Kerkhoff AD, Burton R, Schutz C, Boulle A, Van Wyk G, Blumenthal L, Nicol MP, Lawn SD. 2015. HIV-related medical admissions to a South African district hospital remain frequent despite effective antiretroviral therapy scale-up. Medicine (Baltimore) 94:e2269. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000002269. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Roberts JA, Abdul-Aziz MH, Lipman J, Mouton JW, Vinks AA, Felton TW, Hope WW, Farkas A, Neely MN, Schentag JJ, Drusano G, Frey OR, Theuretzbacher U, Kuti JL. 2014. Individualized antibiotic dosing for patients who are critically ill: challenges and potential solutions. Lancet Infect Dis 14:498–509. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70036-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

