A gut-to-brain signal of fluid osmolarity controls thirst satiation
- PMID: 30918408
- PMCID: PMC6483081
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1066-x
A gut-to-brain signal of fluid osmolarity controls thirst satiation
Abstract
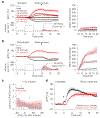
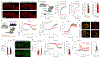
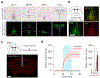
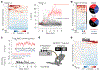
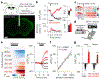
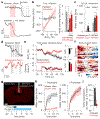
Satiation is the process by which eating and drinking reduce appetite. For thirst, oropharyngeal cues have a critical role in driving satiation by reporting to the brain the volume of fluid that has been ingested1-12. By contrast, the mechanisms that relay the osmolarity of ingested fluids remain poorly understood. Here we show that the water and salt content of the gastrointestinal tract are precisely measured and then rapidly communicated to the brain to control drinking behaviour in mice. We demonstrate that this osmosensory signal is necessary and sufficient for satiation during normal drinking, involves the vagus nerve and is transmitted to key forebrain neurons that control thirst and vasopressin secretion. Using microendoscopic imaging, we show that individual neurons compute homeostatic need by integrating this gastrointestinal osmosensory information with oropharyngeal and blood-borne signals. These findings reveal how the fluid homeostasis system monitors the osmolarity of ingested fluids to dynamically control drinking behaviour.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
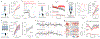
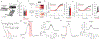
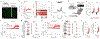



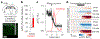


Comment in
-
A thirst-quenching gut-brain signal.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Jun;16(6):327. doi: 10.1038/s41575-019-0147-5. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30980029 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bellows RT Time factors in water drinking in dogs. Am. J. Physiol 125, 87–97, doi:10.1152/ajplegacy.1938.125.1.87 (1938). - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

