Interchangeability of corneal curvature and asphericity measurements provided by three different devices
- PMID: 30918809
- PMCID: PMC6423391
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2019.03.10
Interchangeability of corneal curvature and asphericity measurements provided by three different devices
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the interchangeability of keratometric and asphericity measurements provided by three measurement systems based on different optical principles.
Methods: A total of 40 eyes of 40 patients with a mean age of 34.1y were included. In all cases, a corneal curvature analysis was performed with IOL-Master (IOLM), iDesign 2 (ID2), and Sirius systems (SIR). Differences between instruments for flattest (K1) and steepest (K2) keratometric readings, as well as for magnitude and axis of corneal astigmatism were analyzed. Likewise, differences in asphericity (Q) between SIR and ID2 were also evaluated.
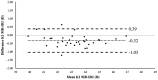
Results: Mean differences between devices for K1 were 0.20±0.21 (P<0.001), -0.12±0.36 (P=0.046) and -0.32±0.36 D (P<0.001) for the comparisons IOLM-SIR, IOLM-ID2 and SIR-ID2, respectively. The ranges of agreement for these comparisons between instruments were 0.41, 0.70, and 0.70 D. For K2, mean differences were 0.31±0.33 (P<0.001), -0.08±0.43 (P=0.265) and -0.39±0.38 D (P<0.001), with ranges of agreement of 0.65, 0.84, and 0.74 D. Concerning magnitude of astigmatism, ranges of agreement were in the limit of clinical relevance (0.49 D, P=0.011; 0.55 D, P=0.386; 0.43 D, P=0.05). In contrast, ranges of agreement were clinically relevant for astigmatic axis (26.68°, 33.83° and 18.37°, P≥0.121) and for Q between SIR and ID2 (0.16, P<0.001).
Conclusion: The keratometric corneal power, astigmatic axis and asphericity measurements provide by the three systems evaluated cannot be considered as interchangeable, whereas measurements of corneal astigmatism obtained with SIR and ID2 can be considered as interchangeable for clinical purposes.
Keywords: astigmatism; corneal asphericity; corneal topography; keratometry.
Figures



References
-
- Piñero DP. Technologies for anatomical and geometric characterization of the corneal structure and anterior segment: a review. Semin Ophthalmol. 2015;30(3):161–170. - PubMed
-
- Ruiz-Belda C, Rodrigo F, Piñero DP. Validation of keratometric measurements obtained with an intraoperative image-guided system: intra-session repeatability and interchangeability with an optical biometer. Clin Exp Optom. 2018;101(2):200–205. - PubMed
-
- Piñero DP, Saenz González C, Alió JL. Intraobserver and interobserver repeatability of curvature and aberrometric measurements of the posterior corneal surface in normal eyes using Scheimpflug photography. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009;35(1):113–120. - PubMed
-
- Güler E, Yağci R, Akyol M, Arslanyılmaz Z, Balci M, Hepşen IF. Repeatability and reproducibility of Galilei measurements in normal keratoconic and postrefractive corneas. Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2014;37(5):331–336. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
