Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Protects Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons against Oxidative Insult
- PMID: 30918901
- PMCID: PMC6408997
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/9426014
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Protects Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons against Oxidative Insult
Abstract
Objective: Diabetic polyneuropathy (DPN) is one of the most prevalent diabetic complications. We previously demonstrated that exendin-4 (Ex4), a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA), has beneficial effects in animal models of DPN. We hypothesized that GLP-1 signaling would protect neurons of the peripheral nervous system from oxidative insult in DPN. Here, the therapeutic potential of GLP-1RAs on DPN was investigated in depth using the cellular oxidative insult model applied to the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neuronal cell line.
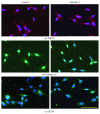
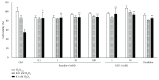
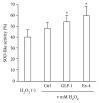
Research design and methods: Immortalized DRG neuronal 50B11 cells were cultured with and without hydrogen peroxide in the presence or absence of Ex4 or GLP-1(7-37). Cytotoxicity and viability were determined using a lactate dehydrogenase assay and MTS (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium inner salt), respectively. Antioxidant enzyme activity was evaluated using a superoxide dismutase assay. Alteration of neuronal characteristics of 50B11 cells induced by GLP-1RAs was evaluated with immunocytochemistry utilizing antibodies for transient receptor potential vanilloid subfamily member 1, substance P, and calcitonin gene-related peptide. Cell proliferation and apoptosis were also examined by ethynyl deoxyuridine incorporation assay and APOPercentage dye, respectively. The neurite projection ratio induced by treatment with GLP-1RAs was counted. Intracellular activation of adenylate cyclase/cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) signaling was also quantified after treatment with GLP-1RAs.
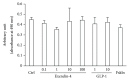
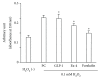
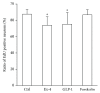
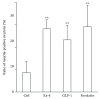
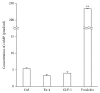
Results: Neither Ex4 nor GLP-1(7-37) demonstrated cytotoxicity in the cells. An MTS assay revealed that GLP-1RAs amended impaired cell viability induced by oxidative insult in 50B11 cells. GLP-1RAs activated superoxide dismutase. GLP-1RAs induced no alteration of the distribution pattern in neuronal markers. Ex4 rescued the cells from oxidative insult-induced apoptosis. GLP-1RAs suppressed proliferation and promoted neurite projections. No GLP-1RAs induced an accumulation of cAMP.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that GLP-1RAs have neuroprotective potential which is achieved by their direct actions on DRG neurons. Beneficial effects of GLP-1RAs on DPN could be related to these direct actions on DRG neurons.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beneficial effects of exendin-4 on experimental polyneuropathy in diabetic mice.Diabetes. 2011 Sep;60(9):2397-406. doi: 10.2337/db10-1462. Epub 2011 Aug 1. Diabetes. 2011. PMID: 21810596 Free PMC article.
-
Exendin-4 Promotes Schwann Cell Survival/Migration and Myelination In Vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 15;22(6):2971. doi: 10.3390/ijms22062971. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33804063 Free PMC article.
-
Glucagon Prevents Cytotoxicity Induced by Methylglyoxal in a Rat Neuronal Cell Line Model.Biomolecules. 2021 Feb 15;11(2):287. doi: 10.3390/biom11020287. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33672050 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the Neuroprotective Role of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Agonists in Diabetic Neuropathy: Current Perspective and Future Directions.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2021;22(1):4-18. doi: 10.2174/1389203721999201208195901. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2021. PMID: 33292149 Review.
-
The extra-pancreatic effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists: a focus on the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal and central nervous systems.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014 Aug;16(8):673-88. doi: 10.1111/dom.12251. Epub 2014 Jan 16. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014. PMID: 24373150 Review.
Cited by
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for the management of diabetic peripheral neuropathy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jan 19;14:1268619. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1268619. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38313844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidative Potentials of Incretin-Based Medications: A Review of Molecular Mechanisms.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Apr 27;2021:9959320. doi: 10.1155/2021/9959320. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34007411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in GLP-1 receptor agonists for pain treatment and their future potential.J Headache Pain. 2025 Feb 27;26(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s10194-025-01979-4. J Headache Pain. 2025. PMID: 40016636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of GLP‑1 receptor agonists in sepsis and their therapeutic potential in sepsis‑induced muscle atrophy (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2025 May;55(5):74. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2025.5515. Epub 2025 Mar 7. Int J Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40052580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immortalized Dorsal Root Ganglion Neuron Cell Lines.Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Jun 19;14:184. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.00184. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32636736 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Genuth S. Insights from the diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study on the use of intensive glycemic treatment to reduce the risk of complications of type 1 diabetes. Endocrine Practice. 2006;12(Supplement 1):34–41. doi: 10.4158/EP.12.S1.34. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

