Mutagenesis Scanning Uncovers Evolutionary Constraints on Tobacco Etch Potyvirus Membrane-Associated 6K2 Protein
- PMID: 30918938
- PMCID: PMC6482416
- DOI: 10.1093/gbe/evz069
Mutagenesis Scanning Uncovers Evolutionary Constraints on Tobacco Etch Potyvirus Membrane-Associated 6K2 Protein
Abstract
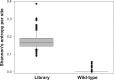
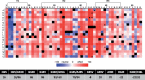
RNA virus high mutation rate is a double-edged sword. At the one side, most mutations jeopardize proteins functions; at the other side, mutations are needed to fuel adaptation. The relevant question then is the ratio between beneficial and deleterious mutations. To evaluate this ratio, we created a mutant library of the 6K2 gene of tobacco etch potyvirus that contains every possible single-nucleotide substitution. 6K2 protein anchors the virus replication complex to the network of endoplasmic reticulum membranes. The library was inoculated into the natural host Nicotiana tabacum, allowing competition among all these mutants and selection of those that are potentially viable. We identified 11 nonsynonymous mutations that remain in the viral population at measurable frequencies and evaluated their fitness. Some had fitness values higher than the wild-type and some were deleterious. The effect of these mutations in the structure, transmembrane properties, and function of 6K2 was evaluated in silico. In parallel, the effect of these mutations in infectivity, virus accumulation, symptoms development, and subcellular localization was evaluated in the natural host. The α-helix H1 in the N-terminal part of 6K2 turned out to be under purifying selection, while most observed mutations affect the link between transmembrane α-helices H2 and H3, fusing them into a longer helix and increasing its rigidity. In general, these changes are associated with higher within-host fitness and development of milder or no symptoms. This finding suggests that in nature selection upon 6K2 may result from a tradeoff between within-host accumulation and severity of symptoms.
Keywords: Potyvirus; TEV; bulk selection; mutagenesis; virulence; virus fitness.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Molecular Biology and Evolution.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The mystery remains: How do potyviruses move within and between cells?Mol Plant Pathol. 2023 Dec;24(12):1560-1574. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13383. Epub 2023 Aug 12. Mol Plant Pathol. 2023. PMID: 37571979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tobacco vein banding mosaic virus 6K2 Protein Hijacks NbPsbO1 for Virus Replication.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 23;7:43455. doi: 10.1038/srep43455. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28230184 Free PMC article.
-
Protein composition of 6K2-induced membrane structures formed during Potato virus A infection.Mol Plant Pathol. 2016 Aug;17(6):943-58. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12341. Epub 2016 Feb 17. Mol Plant Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26574906 Free PMC article.
-
The Vesicle-Forming 6K2 Protein of Turnip Mosaic Virus Interacts with the COPII Coatomer Sec24a for Viral Systemic Infection.J Virol. 2015 Jul;89(13):6695-710. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00503-15. Epub 2015 Apr 15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25878114 Free PMC article.
-
Potyviral 6K2 protein long-distance movement and symptom-induction functions are independent and host-specific.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2004 May;17(5):502-10. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2004.17.5.502. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2004. PMID: 15141954
Cited by
-
AtHVA22a, a plant-specific homologue of Reep/DP1/Yop1 family proteins is involved in turnip mosaic virus propagation.Mol Plant Pathol. 2024 May;25(5):e13466. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13466. Mol Plant Pathol. 2024. PMID: 38767756 Free PMC article.
-
The mystery remains: How do potyviruses move within and between cells?Mol Plant Pathol. 2023 Dec;24(12):1560-1574. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13383. Epub 2023 Aug 12. Mol Plant Pathol. 2023. PMID: 37571979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantifying the Evolutionary Constraints and Potential of Hepatitis C Virus NS5A Protein.mSystems. 2021 Apr 13;6(2):e01111-20. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.01111-20. mSystems. 2021. PMID: 33850042 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase NIb of Potyviruses Plays Multifunctional, Contrasting Roles during Viral Infection.Viruses. 2020 Jan 8;12(1):77. doi: 10.3390/v12010077. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 31936267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small hydrophobic viral proteins involved in intercellular movement of diverse plant virus genomes.AIMS Microbiol. 2020 Sep 21;6(3):305-329. doi: 10.3934/microbiol.2020019. eCollection 2020. AIMS Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33134746 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aguirre J, Manrubia SC.. 2008. Effects of spatial competition on the diversity of a quasispecies. Phys Rev Lett. 100(3):038106.. - PubMed
-
- Ahn S, Vikalo H.. 2018. aBayesQR: a Bayesian method for reconstruction of viral populations characterized by low diversity. J Comput Biol. 25(7):637–648. - PubMed
-
- Bedoya LC, Daròs JA.. 2010. Stability of Tobacco etch virus infectious clones in plasmid vectors. Virus Res. 149(2):234–240. - PubMed

