Evaluation of the child with global developmental delay and intellectual disability
- PMID: 30919832
- PMCID: PMC6234423
- DOI: 10.1093/pch/pxy093
Evaluation of the child with global developmental delay and intellectual disability
Abstract
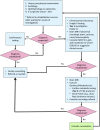
Global developmental delay (GDD) and intellectual disability (ID) are common concerns in the paediatric setting. Etiologies of both conditions are highly heterogeneous. The American Academy of Pediatrics, the American Academy of Neurology and the British Columbia-based Treatable Intellectual Disability Endeavor (TIDE) protocol have each proposed multitiered investigations of GDD/ID to guide physicians toward an understanding of etiology that optimizes therapeutic yield. This statement provides a framework for the clinical investigation of GDD/ID in children, along with an updated protocol for Canadian physicians to follow in the etiological investigation of GDD/ID. The revised protocol is based on current knowledge and existing guidelines. Key elements of investigation include formal vision and hearing testing, chromosomal microarray, Fragile-X DNA testing and first-tier testing for treatable inborn errors of metabolism. Brain imaging is recommended in the presence of specific neurological findings.
Keywords: Chromosome microarray; Global developmental delay; IEM; Intellectual disability.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Intellectual disabilities. In: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th edn Washington, D.C: American Psychiatric Publishing, 2013.
-
- Jimenez-Gomez A, Standridge SM. A refined approach to evaluating global developmental delay for the international medical community. Pediatr Neurol 2014;51(2):198–206. - PubMed
-
- American Academy of Neurology. Evaluation of the Child with Global Developmental Delay 2011. www.aan.com/guidelines (Accessed March 17, 2017).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources