Commissioning of the Mobius3D independent dose verification system for TomoTherapy
- PMID: 30920130
- PMCID: PMC6523001
- DOI: 10.1002/acm2.12572
Commissioning of the Mobius3D independent dose verification system for TomoTherapy
Abstract
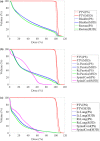
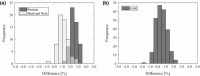
In radiation therapy, a secondary independent dose verification is an important component of a quality control system. Mobius3D calculates three-dimensional (3D) patient dose using reference beam data and a collapsed cone convolution algorithm and analyzes dose-volume histogram automatically. There are currently no published data on commissioning and determining tolerance levels of Mobius3D for TomoTherapy. To verify the calculation accuracy and adjust the parameters of this system, we compared the measured dose using an ion chamber and film in a phantom with the dose calculated using Mobius3D for nine helical intensity-modulated radiation therapy plans, each with three nominal field widths. We also compared 126 treatment plans used in our institution to treat prostate, head-and-neck, and esophagus tumors based on dose calculations by treatment planning system for given dose indices and 3D gamma passing rates with those produced by Mobius3D. On the basis of these results, we showed that the action and tolerance levels at the average dose for the planning target volume (PTV) at each treatment site are at μ ± 2σ and μ ± 3σ, respectively. After adjusting parameters, the dose difference ratio on average was -0.2 ± 0.6% using ion chamber and gamma passing rate with the criteria of 3% and 3 mm on average was 98.8 ± 1.4% using film. We also established action and tolerance levels for the PTV at the prostate, head-and-neck, esophagus, and for the organ at risk at all treatment sites. Mobius3D calculations thus provide an accurate secondary dose verification system that can be commissioned easily and immediately after installation. Before clinical use, the Mobius3D system needs to be commissioned using the treatment plans for patients treated in each institution to determine the calculational accuracy and establish tolerances for each treatment site and dose index.
Keywords: Mobius3D; TomoTherapy; commissioning; independent verification; tolerance.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Stern RL, Heaton R, Fraser MW, et al. Verification of monitor unit calculations for non‐IMRT clinical radiotherapy: report of AAPM Task Group 114. Med Phys. 2011;38:504–530. - PubMed
-
- Kung JH, Chen GT, Kuchnir FK. A monitor unit verification calculation in intensity modulated radiotherapy as a dosimetry quality assurance. Med Phys. 2000;27:2226–2230. - PubMed
-
- Otto K. Volumetric modulated arc therapy: IMRT in a single gantry arc. Med Phys. 2008;35:310–317. - PubMed
-
- Mackie TR. History of tomotherapy. Phys Med Biol. 2006;51:R427–R453. - PubMed
-
- Balog J, Olivera G, Kapatoes J. Clinical helical tomotherapy commissioning dosimetry. Med Phys. 2003;30:3097–3106. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

