Traditional Chinese medicine on treating diabetic mellitus erectile dysfunction: Protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 30921189
- PMCID: PMC6456142
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014928
Traditional Chinese medicine on treating diabetic mellitus erectile dysfunction: Protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Diabetic mellitus erectile dysfunction (DMED) refers to erectile dysfunction (ED) secondary to diabetes. As people's lifestyle changes and the population ages, the incidence of DMED continues to increase. Many clinical trials have proven that Chinese medicine has a significant effect in the treatment of DMED. In this systematic review, we aim to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) for DMED.
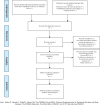
Methods: We will search PubMed, Cochrane Library, AMED, EMbase, WorldSciNet; Nature, Science online and China Journal Full-text Database, China Biomedical Literature CD-ROM Database, and related randomized controlled trials included in the China Resources Database. The time is limited from the construction of the library to February, 2019.We will use the criteria provided by Cochrane 5.1.0 for quality assessment and risk assessment of the included studies, and use the Revman 5.3 and Stata13.0 software for meta-analysis of the effectiveness, recurrence rate, and symptom scores of DMED.
Ethics and dissemination: This systematic review will evaluate the efficacy and safety of TCM for treating Diabetic mellitus erectile dysfunction. Because all of the data used in this systematic review and meta-analysis has been published, this review does not require ethical approval. Furthermore, all data will be analyzed anonymously during the review process trial.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
-
- Chitaley K. Type 1 and type 2 diabetic-erectile dysfunction: same diagnosis (ICD-9), different disease? J Sex Med 2009;6(S3):262–8. - PubMed
-
- Hamdan FB, Almatubsi HY. Assessment of erectile dysfunction in diabetic patients. Int J Androl 2010;32:176–85. - PubMed
-
- Browne DL, Meeking DR, Allard S, et al. Diabetic mellitus erectile dysfunction: an indicator of generalised endothelial function per se? Int J Clin Pract 2010;60:1323–6. - PubMed
-
- De Berardis G, Franciosi M, Belfiglio M, et al. Erectile dysfunction and quality of life in type 2 diabetic patients: a serious problem too often overlooked. Diabetes Care 2002;25:284–91. - PubMed
-
- Musicki B, Burnett AL. Endothelial dysfunction in diabetic mellitus erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 2007;19:129–38. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials