The meiotic phosphatase GSP-2/PP1 promotes germline immortality and small RNA-mediated genome silencing
- PMID: 30921322
- PMCID: PMC6456222
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008004
The meiotic phosphatase GSP-2/PP1 promotes germline immortality and small RNA-mediated genome silencing
Abstract
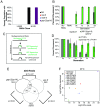
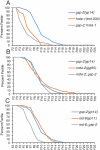
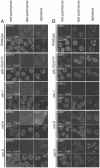
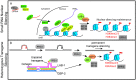
Germ cell immortality, or transgenerational maintenance of the germ line, could be promoted by mechanisms that could occur in either mitotic or meiotic germ cells. Here we report for the first time that the GSP-2 PP1/Glc7 phosphatase promotes germ cell immortality. Small RNA-induced genome silencing is known to promote germ cell immortality, and we identified a separation-of-function allele of C. elegans gsp-2 that is compromised for germ cell immortality and is also defective for small RNA-induced genome silencing and meiotic but not mitotic chromosome segregation. Previous work has shown that GSP-2 is recruited to meiotic chromosomes by LAB-1, which also promoted germ cell immortality. At the generation of sterility, gsp-2 and lab-1 mutant adults displayed germline degeneration, univalents, histone methylation and histone phosphorylation defects in oocytes, phenotypes that mirror those observed in sterile small RNA-mediated genome silencing mutants. Our data suggest that a meiosis-specific function of GSP-2 ties small RNA-mediated silencing of the epigenome to germ cell immortality. We also show that transgenerational epigenomic silencing at hemizygous genetic elements requires the GSP-2 phosphatase, suggesting a functional link to small RNAs. Given that LAB-1 localizes to the interface between homologous chromosomes during pachytene, we hypothesize that small localized discontinuities at this interface could promote genomic silencing in a manner that depends on small RNAs and the GSP-2 phosphatase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
LAB-1 antagonizes the Aurora B kinase in C. elegans.Genes Dev. 2008 Oct 15;22(20):2869-85. doi: 10.1101/gad.1691208. Genes Dev. 2008. PMID: 18923084 Free PMC article.
-
Caenorhabditis elegans RSD-2 and RSD-6 promote germ cell immortality by maintaining small interfering RNA populations.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Oct 14;111(41):E4323-31. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1406131111. Epub 2014 Sep 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25258416 Free PMC article.
-
LAB-1 targets PP1 and restricts Aurora B kinase upon entrance into meiosis to promote sister chromatid cohesion.PLoS Biol. 2012;10(8):e1001378. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001378. Epub 2012 Aug 21. PLoS Biol. 2012. PMID: 22927794 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of germ cell survival and plasticity in Caenorhabditis elegans.Biochem Soc Trans. 2022 Oct 31;50(5):1517-1526. doi: 10.1042/BST20220878. Biochem Soc Trans. 2022. PMID: 36196981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meiotic silencing in Caenorhabditis elegans.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2010;282:91-134. doi: 10.1016/S1937-6448(10)82002-7. Epub 2010 Jun 18. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20630467 Review.
Cited by
-
SDS-22 stabilizes the PP1 catalytic subunits GSP-1/-2 contributing to polarity establishment in C. elegans embryos.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 14:2025.01.07.631699. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.07.631699. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40654901 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
HIM-17 regulates the position of recombination events and GSP-1/2 localization to establish short arm identity on bivalents in meiosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Apr 27;118(17):e2016363118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2016363118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33883277 Free PMC article.
-
Accurate determination of node and arc multiplicities in de bruijn graphs using conditional random fields.BMC Bioinformatics. 2020 Sep 14;21(1):402. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-03740-x. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 32928110 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effect of ubiquitous and germline depletion of Integrator complex function on C. elegans physiology.Biol Open. 2025 Apr 15;14(4):bio061930. doi: 10.1242/bio.061930. Epub 2025 Apr 10. Biol Open. 2025. PMID: 40071568 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional adaptation in Caenorhabditis elegans.Elife. 2020 Jan 17;9:e50014. doi: 10.7554/eLife.50014. Elife. 2020. PMID: 31951195 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed S, Hodgkin J. MRT-2 checkpoint protein is required for germline immortality and telomere replication in C. elegans. Nature. 2000; 159–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

