Synthetic sulfonated derivatives of poly(allylamine hydrochloride) as inhibitors of human metapneumovirus
- PMID: 30921418
- PMCID: PMC6438514
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0214646
Synthetic sulfonated derivatives of poly(allylamine hydrochloride) as inhibitors of human metapneumovirus
Abstract
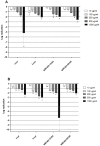
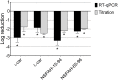
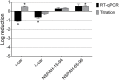
Human metapneumovirus (hMPV) is a widely distributed pathogen responsible for acute upper and lower respiratory infections of varying severity. Previously, we reported that N-sulfonated derivatives of poly(allylamine hydrochloride) (NSPAHs) efficiently inhibit replication of the influenza virus in vitro and ex vivo. Here, we show a dose dependent inhibition of hMPV infection by NSPAHs in LLC-MK2 cells. The results showed strong antiviral properties of NSPAHs. While the activity of NSPAHs is comparable to those of carrageenans, they show better physicochemical properties and may be delivered at high concentrations. The functional assays showed that tested polymers block hMPV release from infected cells and, consequently, constrain virus spread. Moreover, further studies on viruses utilizing different egress mechanisms suggest that observed antiviral effect depend on selective inhibition of viruses budding from the cell surface.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

