A Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis of Aramany Class I Obturator Fabricated with Different Alloys
- PMID: 30923427
- PMCID: PMC6398312
- DOI: 10.4103/jpbs.JPBS_226_18
A Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis of Aramany Class I Obturator Fabricated with Different Alloys
Abstract
Aim: The aim of the research was to develop a model that accurately represents an Aramany class I defect and its obturator prostheses fabricated with cobalt-chromium alloy and titanium alloy to compare the deflection and the stress distribution in the rehabilitated area.
Materials and methods: Aramany class I defect and the obturator prostheses were generated geometrically using ANSYS 14.5; both were superimposed on each other to mimic the prostheses and the maxilla as one unit. Meshing of models was carried out using hypermesh software and materialistic properties were assigned. The 120 newton load was constituted on the teeth in different directions.
Statistical analysis used: Statistical analysis of Finite element was not possible. Self-explanatory decoding results in the software were used.
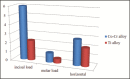
Results: The stress distribution and deflection executed by ANSYS provided results that enabled the tracing of Von Mises stress and deflection field in the form of color-coded bands with values in mega pascal.
Conclusions: The study shows that Von Mises stresses are higher for the frame work fabricated with cobalt-chromium alloy compared to titanium alloy. The framework made of titanium alloy showed more deflection than cobalt-chromium alloy.
Keywords: Aramany class I defect; Von Mises stresses; cobalt–chromium alloy; finite element analysis; titanium alloy.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Miyashita ER, Mattos BS, Noritomi PY, Navarro H. Finite element analysis of maxillary bone stress caused by Aramany Class IV obturator prostheses. J Prosthet Dent. 2012;107:336–42. - PubMed
-
- Parr GR, Tharp GE, Rahn AO. Prosthodontic principles in the framework design of maxillary obturator prostheses. J Prosthet Dent. 2005;93:405–11. - PubMed
-
- Martin-Fernandez E, Gonzalez-Gonzalez I, deLlanos-Lanchares H, Mauvezin-Quevedo MA, Brizuela-Velasco A, Alvarez-Arenal A. Mandibular flexure and peri-implant bone stress distribution on an implant-supported fixed full-arch mandibular prosthesis: 3D finite element analysis. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:8241313. - PMC - PubMed

