Critically important antibiotics: criteria and approaches for measuring and reducing their use in food animal agriculture
- PMID: 30924540
- PMCID: PMC6850619
- DOI: 10.1111/nyas.14058
Critically important antibiotics: criteria and approaches for measuring and reducing their use in food animal agriculture
Abstract
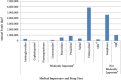
Globally, increasing acquired antimicrobial resistance among pathogenic bacteria presents an urgent challenge to human and animal health. As a result, significant efforts, such as the One Health Initiative, are underway to curtail and optimize the use of critically important antimicrobials for human medicine in all applications, including food animal production. This review discusses the rationale behind multiple and competing "critically important antimicrobial" lists and their contexts as created by international, regional, and national organizations; identifies discrepancies among these lists; and describes issues surrounding risk management recommendations that have been made by regulatory organizations on the use of antibiotics in food animal production. A more harmonized approach to defining criticality in its various contexts (e.g., for human versus animal health, enteric diseases versus other systemic infections, and direct versus indirect selection of resistance) is needed in order to identify shared contextual features, aid in their translation into risk management, and identify the best ways to maintain the health of food animals, all while keeping in mind the wider risks of antimicrobial resistance, environmental impacts, and animal welfare considerations.
Keywords: animal agriculture; antimicrobial resistance; antimicrobials; critically important antimicrobials.
© 2019 The Authors. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of New York Academy of Sciences.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . 2017. WHO list of critically important antimicrobials for human medicine (WHO CIA list). 5th revision. World Health Organization.
-
- World Health Organization . 2017. WHO guidelines on use of medically important antimicrobials in food‐producing animals. WHO. - PubMed
-
- World Organisation for Animal Health . 2015. OIE list of antimicrobial agents of veterinary importance. OIE International Committee. Vol. 33, pp. 1–9.
-
- Food Safety Commission of Japan . 2014. Ranking of the importance of antimicrobials against bacteria which affect human health through food commodities.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

