Thyroxine (T4) may promote re-epithelialisation and angiogenesis in wounded human skin ex vivo
- PMID: 30925152
- PMCID: PMC6440638
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212659
Thyroxine (T4) may promote re-epithelialisation and angiogenesis in wounded human skin ex vivo
Abstract
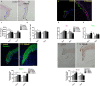
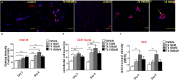
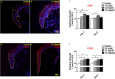
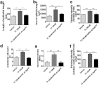
There is a pressing need for improved preclinical model systems in which to study human skin wound healing. Here, we report the development and application of a serum-free full thickness human skin wound healing model. Not only can re-epithelialization (epidermal repair) and angiogenesis be studied in this simple and instructive model, but the model can also be used to identify clinically relevant wound-healing promoting agents, and to dissect underlying candidate mechanisms of action in the target tissue. We present preliminary ex vivo data to suggest that Thyroxine (T4), which reportedly promotes skin wound healing in rodents in vivo, may promote key features of human skin wound healing. Namely, T4 stimulates re-epithelialisation and angiogenesis, and modulates both wound healing-associated epidermal keratin expression and energy metabolism in experimentally wound human skin. Functionally, the wound healing-promoting effects of T4 are at least partially mediated via fibroblast growth factor/fibroblast growth factor receptor-mediated signalling, since they could be significantly antagonized by bFGF-neutralizing antibody. Thus, this pragmatic, easy-to-use full-thickness human skin wound healing model provides a useful preclinical research tool in the search for clinically relevant candidate wound healing-promoting agents. These ex vivo data encourage further pre-clinical testing of topical T4 as a cost-efficient, novel agent in the management of chronic human skin wounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Ilonzo N, Patel M, Lantis JC 2nd. Managing the Diabetic Foot Ulcer: How Best Practices Fit the Real 2018 United States. Surg Technol Int. 2018;32:49–59. Epub 2018/04/04. . - PubMed
-
- Coleman S, Smith IL, McGinnis E, Keen J, Muir D, Wilson L, et al. Clinical evaluation of a new pressure ulcer risk assessment instrument, the Pressure Ulcer Risk Primary or Secondary Evaluation Tool (PURPOSE T). J Adv Nurs. 2018;74(2):407–24. Epub 2017/08/24. 10.1111/jan.13444 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

