Small-molecule factor B inhibitor for the treatment of complement-mediated diseases
- PMID: 30926668
- PMCID: PMC6475383
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1820892116
Small-molecule factor B inhibitor for the treatment of complement-mediated diseases
Abstract
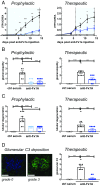
Dysregulation of the alternative complement pathway (AP) predisposes individuals to a number of diseases including paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome, and C3 glomerulopathy. Moreover, glomerular Ig deposits can lead to complement-driven nephropathies. Here we describe the discovery of a highly potent, reversible, and selective small-molecule inhibitor of factor B, a serine protease that drives the central amplification loop of the AP. Oral administration of the inhibitor prevents KRN-induced arthritis in mice and is effective upon prophylactic and therapeutic dosing in an experimental model of membranous nephropathy in rats. In addition, inhibition of factor B prevents complement activation in sera from C3 glomerulopathy patients and the hemolysis of human PNH erythrocytes. These data demonstrate the potential therapeutic value of using a factor B inhibitor for systemic treatment of complement-mediated diseases and provide a basis for its clinical development.
Keywords: alternative pathway; complement; drug discovery; factor B; nephropathy.
Copyright © 2019 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: Novartis Pharma AG has filed patent applications on the compounds. A.S., K.A., N.M., H.S., T.E., C.M.A., A.M.S., S.-M.L., M.C., A.L.-E., S.S., G.W., L.P., V.D., T.F., R.G.K., C.Z., E.V., F.S., B.G., P.E., N.H., T.M.S., F.C., U.A.A., B.H., M.M., R.S., C.W., B.J., J.M., S.F., R.H., and J.E. are or were employees of Novartis Pharma AG during this work.
Figures
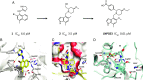


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

