Action of MK-7264 (gefapixant) at human P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptors and in vivo efficacy in models of sensitisation
- PMID: 30927255
- PMCID: PMC6555852
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.14677
Action of MK-7264 (gefapixant) at human P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptors and in vivo efficacy in models of sensitisation
Abstract
Background and purpose: The P2X3 receptor is an ATP-gated ion channel expressed by sensory afferent neurons and is used as a target to treat chronic sensitisation conditions. The first-in-class, selective P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptor antagonist, the diaminopyrimidine MK-7264 (gefapixant), has progressed to Phase III trials for refractory or unexplained chronic cough. We used patch clamp to elucidate the pharmacology and kinetics of MK-7264 and rat models of hypersensitivity and hyperalgesia to test its efficacy on these conditions.
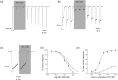
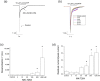
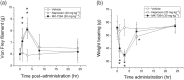
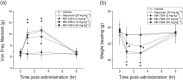
Experimental approach: Whole-cell patch clamp of 1321N1 cells expressing human P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptors was used to determine mode of MK-7264 action, potency, and kinetics. The analgesic efficacy was assessed using paw withdrawal threshold and limb weight distribution in rat models of inflammatory, osteoarthritic, and neuropathic sensitisation.
Key results: MK-7264 is a reversible allosteric antagonist at human P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptors. Experiments with the slowly desensitising P2X2/3 heteromer revealed concentration- and state-dependency to wash-on, with faster rates and greater inhibition when applied before agonist compared to during agonist application. The wash-on rate (τ value) for MK-7264 at maximal concentrations was much lower when applied before compared to during agonist application. In vivo, MK-7264 displayed efficacy comparable to naproxen in inflammatory and osteoarthritic sensitisation models and gabapentin in neuropathic sensitisation models, increasing paw withdrawal threshold and decreasing weight-bearing discomfort.
Conclusions and implications: MK-7264 is a reversible and selective P2X3 and P2X2/3 antagonist, exerting allosteric antagonism via preferential activity at closed channels. Its efficacy in rat models supports its clinical investigation for chronic sensitisation conditions.
© 2019 The British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abdulqawi, R. , Dockry, R. , Holt, K. , Layton, G. , McCarthy, B. G. , Ford, A. P. , & Smith, J. A. (2015). P2X3 receptor antagonist (AF‐219) in refractory chronic cough: A randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled phase 2 study. The Lancet, 385, 1198–1205. - PubMed
-
- Barclay, J. , Patel, S. , Dorn, G. , Wotherspoon, G. , Moffatt, S. , Eunson, L. , … Ganju, P. (2002). Functional downregulation of P2X3 receptor subunit in rat sensory neurons reveals a significant role in chronic neuropathic and inflammatory pain. Journal of Neuroscience, 22(18), 8139–8147. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-18-08139.2002 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bove, S. E. , Calcaterra, S. L. , Brooker, R. M. , Huber, C. M. , Guzman, R. E. , Juneau, P. L. , … Kilgore, K. S. (2003). Weight bearing as a measure of disease progression and efficacy of anti‐inflammatory compounds in a model of monosodium iodoacetate‐induced osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage., 11, 821–830. 10.1016/S1063-4584(03)00163-8 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

