A Common Embryonic Origin of Stem Cells Drives Developmental and Adult Neurogenesis
- PMID: 30929900
- PMCID: PMC6496946
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.02.010
A Common Embryonic Origin of Stem Cells Drives Developmental and Adult Neurogenesis
Abstract
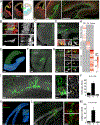
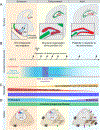
New neurons arise from quiescent adult neural progenitors throughout life in specific regions of the mammalian brain. Little is known about the embryonic origin and establishment of adult neural progenitors. Here, we show that Hopx+ precursors in the mouse dentate neuroepithelium at embryonic day 11.5 give rise to proliferative Hopx+ neural progenitors in the primitive dentate region, and they, in turn, generate granule neurons, but not other neurons, throughout development and then transition into Hopx+ quiescent radial glial-like neural progenitors during an early postnatal period. RNA-seq and ATAC-seq analyses of Hopx+ embryonic, early postnatal, and adult dentate neural progenitors further reveal common molecular and epigenetic signatures and developmental dynamics. Together, our findings support a "continuous" model wherein a common neural progenitor population exclusively contributes to dentate neurogenesis throughout development and adulthood. Adult dentate neurogenesis may therefore represent a lifelong extension of development that maintains heightened plasticity in the mammalian hippocampus.
Keywords: Hopx; brain development; chromatin landscape profiling; dentate gyrus; gene expression profiling; hippocampus; lineage tracing; neural stem cells; neurogenesis.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Comment in
-
All Roads Lead to Rome: Hippocampal Stem Cells Hop(x) the Continuous Way.Cell Stem Cell. 2019 May 2;24(5):683-684. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2019.04.013. Cell Stem Cell. 2019. PMID: 31051131
References
-
- Altman J, and Bayer SA (1990). Mosaic organization of the hippocampal neuroepithelium and the multiple germinal sources of dentate granule cells. The Journal of comparative neurology 301, 325–342. - PubMed
-
- Bayer SA, and Altman J (1974). Hippocampal development in the rat: cytogenesis and morphogenesis examined with autoradiography and low-level X-irradiation. The Journal of comparative neurology 158, 55–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

