Clinically Relevant Correction of Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa by Dual sgRNA CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Gene Editing
- PMID: 30930113
- PMCID: PMC6520462
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.03.007
Clinically Relevant Correction of Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa by Dual sgRNA CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Gene Editing
Abstract
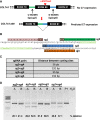
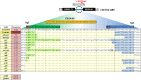
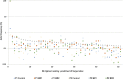
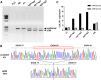
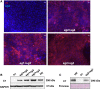
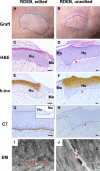
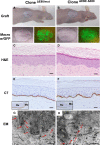
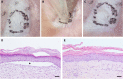
Gene editing constitutes a novel approach for precisely correcting disease-causing gene mutations. Frameshift mutations in COL7A1 causing recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa are amenable to open reading frame restoration by non-homologous end joining repair-based approaches. Efficient targeted deletion of faulty COL7A1 exons in polyclonal patient keratinocytes would enable the translation of this therapeutic strategy to the clinic. In this study, using a dual single-guide RNA (sgRNA)-guided Cas9 nuclease delivered as a ribonucleoprotein complex through electroporation, we have achieved very efficient targeted deletion of COL7A1 exon 80 in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB) patient keratinocytes carrying a highly prevalent frameshift mutation. This ex vivo non-viral approach rendered a large proportion of corrected cells producing a functional collagen VII variant. The effective targeting of the epidermal stem cell population enabled long-term regeneration of a properly adhesive skin upon grafting onto immunodeficient mice. A safety assessment by next-generation sequencing (NGS) analysis of potential off-target sites did not reveal any unintended nuclease activity. Our strategy could potentially be extended to a large number of COL7A1 mutation-bearing exons within the long collagenous domain of this gene, opening the way to precision medicine for RDEB.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; epidermal stem cells; epidermolysis bullosa; gene therapy.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Fine J.D., Bruckner-Tuderman L., Eady R.A., Bauer E.A., Bauer J.W., Has C., Heagerty A., Hintner H., Hovnanian A., Jonkman M.F. Inherited epidermolysis bullosa: updated recommendations on diagnosis and classification. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014;70:1103–1126. - PubMed
-
- Bauer J.W., Koller J., Murauer E.M., De Rosa L., Enzo E., Carulli S., Bondanza S., Recchia A., Muss W., Diem A. Closure of a Large Chronic Wound through Transplantation of Gene-Corrected Epidermal Stem Cells. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2017;137:778–781. - PubMed
-
- Mavilio F., Pellegrini G., Ferrari S., Di Nunzio F., Di Iorio E., Recchia A., Maruggi G., Ferrari G., Provasi E., Bonini C. Correction of junctional epidermolysis bullosa by transplantation of genetically modified epidermal stem cells. Nat. Med. 2006;12:1397–1402. - PubMed
-
- Siprashvili Z., Nguyen N.T., Gorell E.S., Loutit K., Khuu P., Furukawa L.K., Lorenz H.P., Leung T.H., Keene D.R., Rieger K.E. Safety and Wound Outcomes Following Genetically Corrected Autologous Epidermal Grafts in Patients With Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa. JAMA. 2016;316:1808–1817. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

