CHD1 Loss Alters AR Binding at Lineage-Specific Enhancers and Modulates Distinct Transcriptional Programs to Drive Prostate Tumorigenesis
- PMID: 30930119
- PMCID: PMC6467783
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.03.001
CHD1 Loss Alters AR Binding at Lineage-Specific Enhancers and Modulates Distinct Transcriptional Programs to Drive Prostate Tumorigenesis
Erratum in
-
CHD1 Loss Alters AR Binding at Lineage-Specific Enhancers and Modulates Distinct Transcriptional Programs to Drive Prostate Tumorigenesis.Cancer Cell. 2019 May 13;35(5):817-819. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.04.012. Cancer Cell. 2019. PMID: 31085180 No abstract available.
Abstract
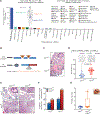
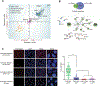
Deletion of the gene encoding the chromatin remodeler CHD1 is among the most common alterations in prostate cancer (PCa); however, the tumor-suppressive functions of CHD1 and reasons for its tissue-specific loss remain undefined. We demonstrated that CHD1 occupied prostate-specific enhancers enriched for the androgen receptor (AR) and lineage-specific cofactors. Upon CHD1 loss, the AR cistrome was redistributed in patterns consistent with the oncogenic AR cistrome in PCa samples and drove tumor formation in the murine prostate. Notably, this cistrome shift was associated with a unique AR transcriptional signature enriched for pro-oncogenic pathways unique to this tumor subclass. Collectively, these data credential CHD1 as a tumor suppressor in the prostate that constrains AR binding/function to limit tumor progression.
Keywords: AR; CHD1; HOXB13; androgen receptor; chromatin remodeling; cistrome reprogramming; epigenetics; interactome; prostate cancer; prostate cancer subclass.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


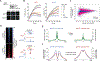


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

