Verifying OpenJDK's Sort Method for Generic Collections
- PMID: 30930511
- PMCID: PMC6404383
- DOI: 10.1007/s10817-017-9426-4
Verifying OpenJDK's Sort Method for Generic Collections
Abstract
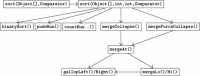
TimSort is the main sorting algorithm provided by the Java standard library and many other programming frameworks. Our original goal was functional verification of TimSort with mechanical proofs. However, during our verification attempt we discovered a bug which causes the implementation to crash by an uncaught exception. In this paper, we identify conditions under which the bug occurs, and from this we derive a bug-free version that does not compromise performance. We formally specify the new version and verify termination and the absence of exceptions including the bug. This verification is carried out mechanically with KeY, a state-of-the-art interactive verification tool for Java. We provide a detailed description and analysis of the proofs. The complexity of the proofs required extensions and new capabilities in KeY, including symbolic state merging.
Keywords: Case study; Program verification; Specification; Theorem proving.
Figures


References
-
- Ahrendt W, Beckert B, Bubel R, Hähnle R, Schmitt P, Ulbrich M, editors. Deductive Software Verification—The KeY Book: From Theory to Practice, LNCS. Berlin: Springer; 2016.
-
- Ahrendt, W., Mostowski, W., Paganelli, G.: Real-time Java API specifications for high coverage test generation. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Workshop on Java Technologies for Real-Time and Embedded Systems, JTRES ’12, pp. 145–154. ACM, New York (2012)
-
- Akbarpour B, Abdel-Hamid AT, Tahar S, Harrison J. Verifying a synthesized implementation of IEEE-754 floating-point exponential function using HOL. Comput. J. 2010;53(4):465–488. doi: 10.1093/comjnl/bxp023. - DOI
-
- Beckert B, Hähnle R. Reasoning and verification. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2014;29(1):20–29. doi: 10.1109/MIS.2014.3. - DOI
-
- Beckert B, Klebanov V. Proof reuse for deductive program verification. In: Cuellar J, Liu Z, editors. Proceedings, Software Engineering and Formal Methods (SEFM) Beijing: IEEE Press; 2004.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
