Effect of microRNA-21 on hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in orthodontic tooth movement and human periodontal ligament cells under hypoxia
- PMID: 30930976
- PMCID: PMC6425288
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.7248
Effect of microRNA-21 on hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in orthodontic tooth movement and human periodontal ligament cells under hypoxia
Abstract
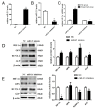
Orthodontic tooth movement can lead to temporary hypoxia of periodontal tissues. Periodontal ligament cells (PDLCs) react to hypoxia, releasing various biological factors to promote periodontal tissue reconstruction. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) is one of the most sensitive factors involved in the response to hypoxia. HIF-1α has been identified to be involved in osteogenic and osteoclast differentiation in vitro; however, few studies have investigated the expression of HIF-1α in the periodontal ligament (PDL) during orthodontic movement in vivo. In a previous study, microRNA-21 (miR-21) was demonstrated to be highly expressed in a rat model of orthodontic tooth movement. Additionally, miR-21 can increase the expression of HIF-1α in certain tumor cell types and is involved in tumor bioactivities. In the present study, HIF-1α exhibited expression patterns in a similar way to miR-21 in PDL samples from a rat model of orthodontic tooth movement, with expression initially increased and followed by a decrease over time. Furthermore, human PDLCs were exposed to a hypoxic environment in vitro, which induced significant upregulation of HIF-1α and miR-21 expression. Furthermore, miR-21 mimics increased HIF-1α expression and promoted osteogenic differentiation, indicated by upregulated expression of the osteogenic markers osteopontin, runt-related gene-2 and alkaline phosphatase. miR-21 inhibitors suppressed HIF-1α expression and downregulated the osteogenic markers. In conclusion, the results revealed that miR-21 has a positive effect on HIF-1α expression in PDLCs under hypoxia and has important roles in osteogenic differentiation during orthodontic tooth movement. These findings provide a theoretical basis by which to promote tissue reconstruction during orthodontic tooth movement.
Keywords: hypoxia; hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; microRNA-21; orthodontic tooth movement; periodontal ligament cells.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
