C-Reactive Protein and Ferritin Are Associated With Organ Dysfunction and Mortality in Hospitalized Children
- PMID: 30931590
- PMCID: PMC7049089
- DOI: 10.1177/0009922819837352
C-Reactive Protein and Ferritin Are Associated With Organ Dysfunction and Mortality in Hospitalized Children
Abstract
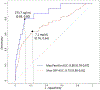
Our objective was to determine if C-reactive protein (CRP) and ferritin values alone and in combination are associated with mortality among hospitalized children. All hospitalized patients at our institution with a CRP or ferritin assay in 2015 and 2016 were included. Area under the receiver operating curves (AUROC) were examined, optimal cut-points determined, and patients were stratified into low-, intermediate-, or high-risk groups based on elevation of zero, one, or both biomarkers. A total of 14 928 CRP and 653 ferritin values were obtained, with both obtained for 172 patients. AUROC for maximum CRP value was 0.76 (0.68-0.85) with a cut-point of 7.1 mg/dL for in-hospital mortality and 0.90 (0.83-0.98) for maximum ferritin with a cut-point of 373 ng/mL. Elevation of both ferritin and CRP was associated with the highest inpatient mortality (21.7%) and greatest organ dysfunction, followed by either biomarker alone. Additional prospective study of these biomarkers in combination is warranted.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; electronic health record; ferritin; learning health system; multiple organ dysfunction.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this article to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- McWilliam S, Riordan A: How to use: C-reactive protein. Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed 2010; 95:55–58 - PubMed
-
- Rey C, Los Arcos M, Concha A, et al.: Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as markers of systemic inflammatory response syndrome severity in critically ill children. Intensive Care Med 2007; 33:477–484 - PubMed
-
- B.Kell D, Pretorius E: Serum ferritin is an important inflammatory disease marker, as it is mainly a leakage product from damaged cells. Metallomics 2014; 6:748–773 - PubMed
-
- Garcia PCR, Longhi F, Branco RG, et al.: Ferritin levels in children with severe sepsis and septic shock. Acta Paediatr Oslo Nor 1992 2007; 96:1829–1831 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

